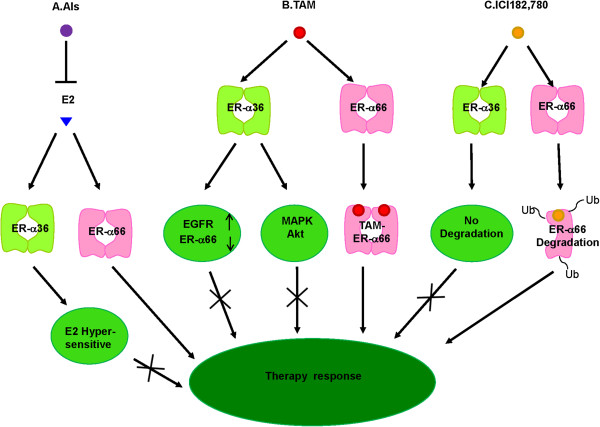
Figure 6.
ER-α36 and endocrine therapy resistance. (A). Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) inhibit the synthesis of estrogen. High expression of ER-α36 contributes to estrogen hypersensitivity. This provides an explanation for failure of AIs treatment in ER-negative breast cancer patients. (B). Tamoxifen (TAM) inhibits ER-mediated mitogenic estrogen signaling by competing with estrogens (E2) for the ligand binding domain of ER-α66. The non-genomic activities of ER-α36 are involved in de novo TAM resistance of breast cancer. Up-regulation of EGFR expression and down-regulation of ER-α66 expression by ER-α36 could contribute to generation of acquired TAM resistance. (C). ICI 182,780 can accelerate degradation of ER-α66 protein so as to inhibit mediated estrogen signaling. However, ICI182,780 fails to induce degradation of ER-α36 to take therapeutic effect. AIs: Aromatase inhibitors TAM: Tamoxifen