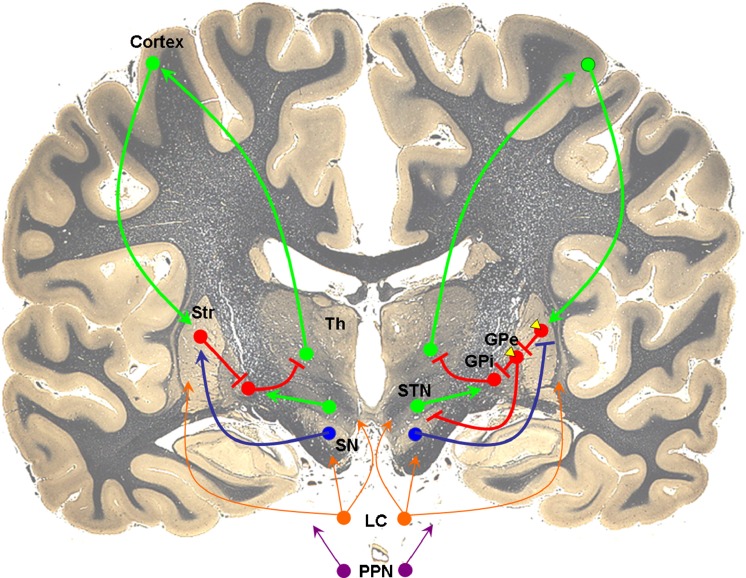
Fig. 1.
Neurotransmitter systems involved in basal ganglia circuitry. Excitatory glutamatergic efferents (green) from cortex project to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic (red) striatal neurons. In the direct pathway (left), striatal neurons receive excitatory dopaminergic inputs (blue) from substantia nigra and project directly to globus pallidus interna (GPi). In the indirect pathway (right), dopamine inhibits striatal GABAergic output to the globus pallidus externa (GPe), which then projects to GPi. Adenosine A2A receptors (yellow) are localized to dopamine D2 receptor-containing cells in the indirect pathway. Noradrenergic and cholinergic efferents from the locus coeruleus (orange) and pedunculopontine nucleus (purple), respectively, project widely to multiple brain regions, including cortex and basal ganglia. The coronal brain image is adapted with permission from http://www.brains.rad.msu.edu and http://brainmuseum.org, supported by the US National Science Foundation