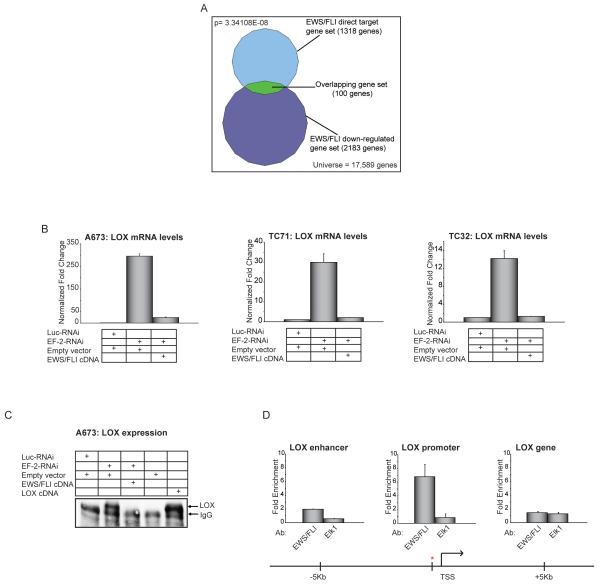
Figure 1. Identification of direct downregulated targets of EWS/FLI.
(A) Venn diagram representation of the overlap between EWS/FLI downregulated genes (by transcriptional profiling) and EWS/FLI direct targets (by ChIP-chip) in A673 Ewing sarcoma cells. The Chi square-determined p-value is indicated.
(B) qRT-PCR validation of EWS/FLI mediated transcriptional repression of LOX in A673, TC71 and TC32 Ewing sarcoma cells following retroviral knockdown of endogenous EWS/FLI (EF-2-RNAi, versus the negative-control Luc-RNAi) and rescue with an RNAi-resistant EWS/FLI cDNA (versus an empty vector control). Error bars indicate standard deviations. Normalized fold enrichment was calculated by determining the fold-change of each condition relative to the control Luc-RNAi condition, with the data in each condition normalized to an internal housekeeping control gene GAPDH.
(C) Immunoprecipitation-Western blot analysis of LOX protein from A673 cells expressing the indicated RNAi constructs (Luc-RNAi negative-control versus EWS/FLI knockdown with EF-2-RNAi), and the indicated expression vectors (empty vector negative control, EWS/FLI cDNA resistant to the RNAi construct, or a LOX cDNA). The same antibody was used to perform the immunoprecipitation and the Western blotting. The IgG band refers to the heavy chain.
(D) ChIP of EWS/FLI at the LOX locus using antibodies against FLI (which recognizes only EWS/FLI) or ELK1 (negative control). The ChIP experiments were performed in A673 Ewing sarcoma cells which express EWS/FLI but do not have any detectable expression of wild-type FLI (7), and so the anti-FLI antibody used only detects the fusion protein. Thus, there is no competition between the two transcription factors for the same binding sites. The red asterisk indicates the ChIP-Chip identified EWS/FLI binding site at the LOX promoter, and the transcriptional start site (TSS) is indicated. The level of enrichment for EWS/FLI or ELK1 are plotted as fold enrichment compared to the average enrichment of EWS/FLI or ELK1 at two negative control housekeeping genes ALB and BCL2L1 used as normalization controls. Elk1 immunoprecipitation is used as a negative control for the ChIP experiment. Enrichment of EWS/FLI or Elk1 at regions 5 kb upstream and downstream of the ChIP-Chip identified binding site were used as negative controls to further demonstrate binding specificity for EWS/FLI at the LOX promoter. The error bars indicate standard error of the means of five independent experiments.