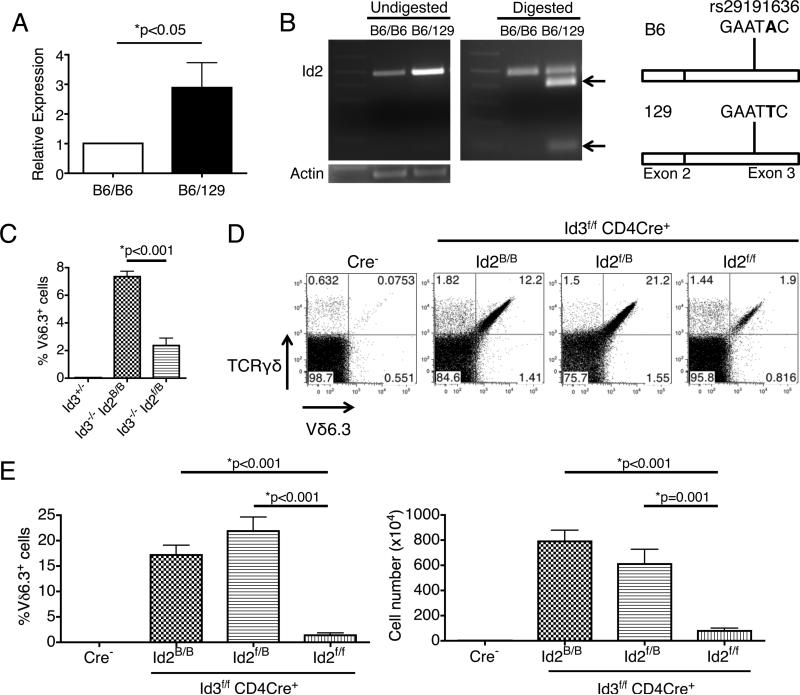
Figure 2.
Id2 is a major modifier of Vδ6.3+ γδ T cell development in Id3-deficient mice. (A) QPCR analysis showed that Id2 mRNA expression in Vδ6.3+ γδ T cells from Id3−/− mice with B6 background on the chromosome 12 region encompassing Id2 is lower than those with B6/129 mix background. n=3 for independent sorting of each genotype group. (B) Restriction enzyme analysis of the SNP marker rs29191636 within the exon 3 of the Id2 gene. EcoRI digestion of Id2 cDNA made from Vδ6.3+ γδ T cells with B6/129 mix background generated abundant product specific to the 129 allele (marked by two arrows), indicating that the higher Id2 expression in these cells came from that allele. Data representative of 3 experiments. (C) Replacement of one copy of the Id2 B6 allele with the Id2f allele of 129 origin is sufficient to reduce the population size of Vδ6.3+ γδ T cells. Id2B indicates the wild type Id2 allele in B6 background. n≥3 for each group. (D) Analysis of Vδ6.3+ γδ T cells with various combinations of Id2B and Id2f alleles on Id3f/f CD4Cre+ background. Data representative of 3 mice in each group. (E) Percentage and number of Vδ6.3+ γδ T cell in the thymus of genotype each group shown in D. N≥4 in each group. All error bars indicate SD.