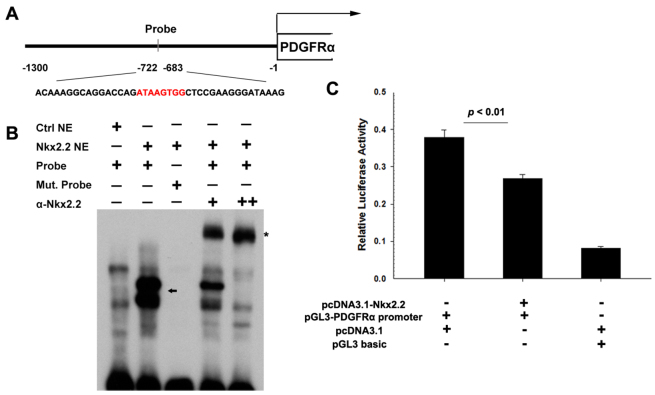
Fig. 4.
Binding and activity assays of Pdgfra promoter. (A) Schematic of the genomic sequence upstream Pdgfra, including the putative promoter cloned into the luciferase vector and selected sequence for EMSA probe (red represents core binding sequence). (B) EMSA analysis of Nkx2.2 binding. Probe (see A) spanning ∼40 bp surrounding the predicted binding sequence was incubated with nuclear extracts from mock-transfected cells (Ctrl NE) or nuclear extracts from transfected cells (Nkx2.2 NE). The core site ATAAGTGG was replaced with TTTTTTTT as mutated probe (Mut. Probe). Supershift experiments were performed using monoclonal anti-Nkx2.2 antibody (α-Nkx2.2). The arrow shows the Nkx2.2-specific-bound complexes with lower mobility. The asterisk marks α-Nkx2.2-Nkx2.2-probe complexes with the lowest mobility. (C) Co-transfection of pcDNA3.1-Nkx2.2 and pGL3-Pdgfra promoter significantly inhibits the luciferase activity (mean ± s.e.m., n=3). Data are normalized using Renilla luciferase.