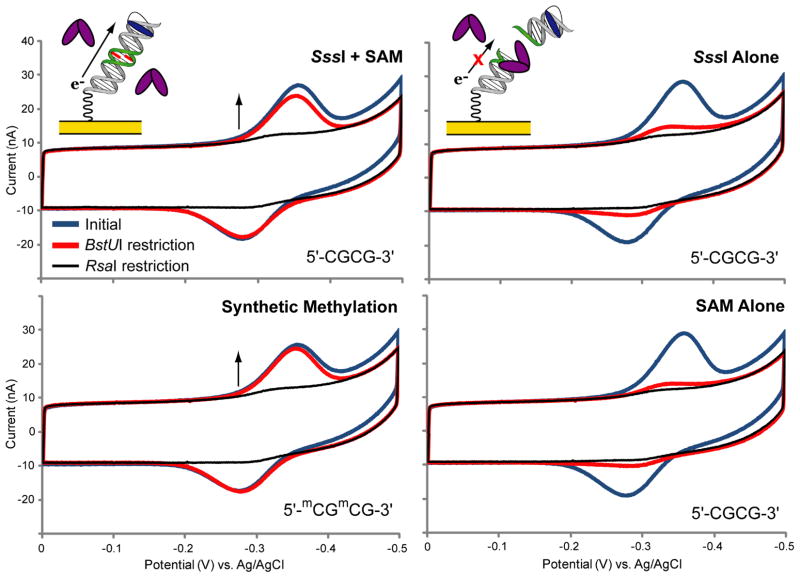
Figure 2.
SssI protection from BstUI restriction is dependent on the SAM cofactor. Chips were modified in three quadrants with the unmethylated BstUI 20-mer (top row and bottom right) and in one quadrant with the synthetically methylated BstUI 20-mer (bottom left). The BstUI 20-mer consists of the sequence 5′-HS- (CH2)6 - GACTGAGTACTCGCGACTGA -3′ with an unmethylated methylene blue-modified complement. The BstUI restriction site (5′-CGCG - 3′) is underlined and the RsaI restriction site (5′-GTAC-3′) is italicized. The synthetically methylated BstUI 20-mer contains a restriction site that is fully methylated on both strands (5′-mCGmCG-3′). DNA protection was evaluated side by side on the same chip: the unmethylated DNA quadrants were treated with 20 nM SssI and 160 μM SAM (top left), 20 nM SssI alone (top right), or 160 μM SAM alone (bottom right), while the synthetically methylated quadrant was left untreated in buffer alone. After an initial CV scan (blue traces), the chip was treated in all quadrants with BstUI (1,000 units/mL) (red traces). Finally, the chip was treated in all quadrants with RsaI (1,000 units/mL) (black traces). All CV scans were performed in M/R buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, pH 7.9) with an Ag/AgCl reference electrode at a 100 mV/s scan rate.