Figure 3.
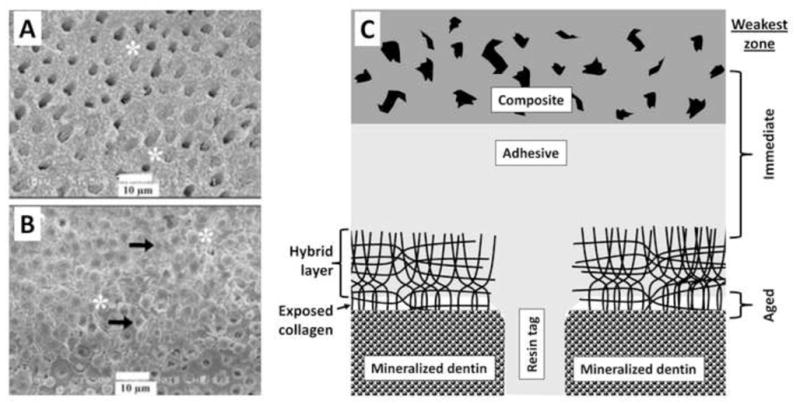
A: SEM image of the fracture occurring at the bottom of the hybrid layer. Dentinal tubules are mostly exposed, with few dentinal tubules containing remaining resin tags. Partially degraded collagen at the bottom of the hybrid layer gives can be seen (asterisk). B: SEM image of the fracture cohesive failure localized in the middle of the hybrid layer. Dentinal tubules are completely filled by resin tags (black arrow), and intertubular dentin is covered by adhesive (asterisk). C: Schematic presentation of resin-bonded acid-etched dentin covered with resin composite. The acid-etched tubules no longer contain peritubular dentin, making the tubules twice their normal diameter. Resin tags extend down from the adhesive layer. The tags are hybridized with the surrounding demineralized dentin as they pass through the hybrid layer. There is no such hybridization of the resin tags as it passes into mineralized dentin. As poorly infiltrated hybrid layers age, the collagen fibrils degrade and disappear. In such hybrid layers, water replaces the collagen. The spaces in the composite are due to hydrolysis of nanofillers of silica from the resin composite. These, too become filled with water. (Figures A and B reproduced from Carrilho et al. 2007 [31], with permission.)
