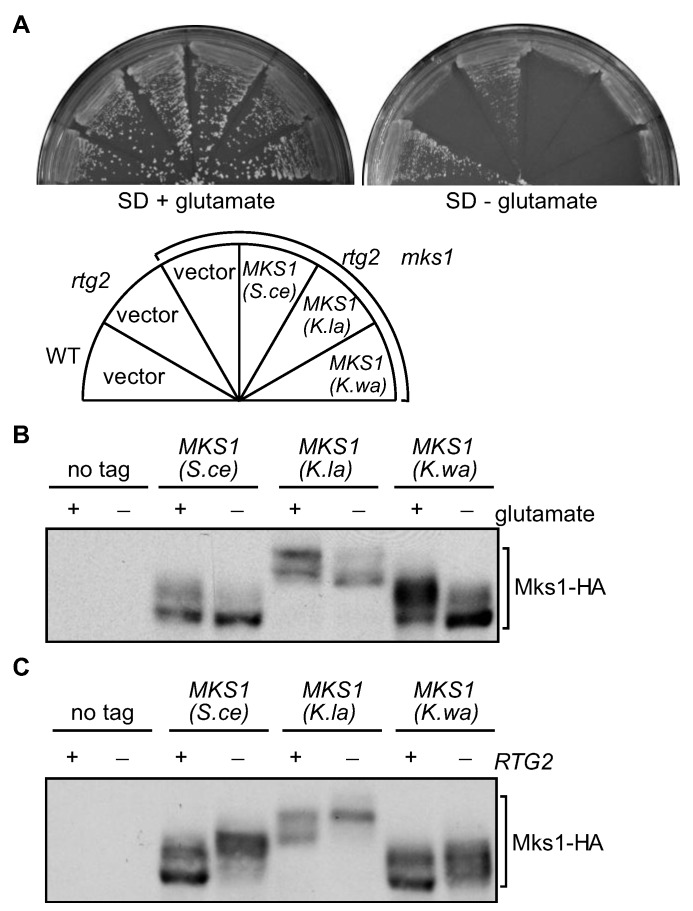
Figure 4.
The function and regulation of Mks1 homologs from K. lactis and K. waltii are conserved. (A) MKS1 homologs from K. lactis (K.la) and K. waltii (K.wa) complement an mks1Δ mutation in S. cerevisiae (S.ce). Yeast strains as indicated were grown on SD medium with or without glutamate at 30 °C for 2 to 3 days. (B) Glutamate has similar effects on the phosphorylation of S. cerevisiae Mks1 and its homologs from K. lactis and K. waltii. mks1Δ mutant cells (ZLY028) carrying centromeric plasmids encoding MKS1 genes from the indicated fungal species were grown in SD medium supplemented with or without glutamate. Total cellular proteins were prepared and separated by SDS-PAGE, and HA-tagged Mks1 was detected by Western-blotting. (C) The absence of RTG2 increases phosphorylation of Mks1. Cells expressing HA-tagged Mks1 from the indicated fungal species without (+ RTG2) or with an rtg2Δ mutation (˗ RTG2) were grown in YNBcasD medium, and phosphorylation of Mks1 was analyzed as described for panel (B).