Figure 1.
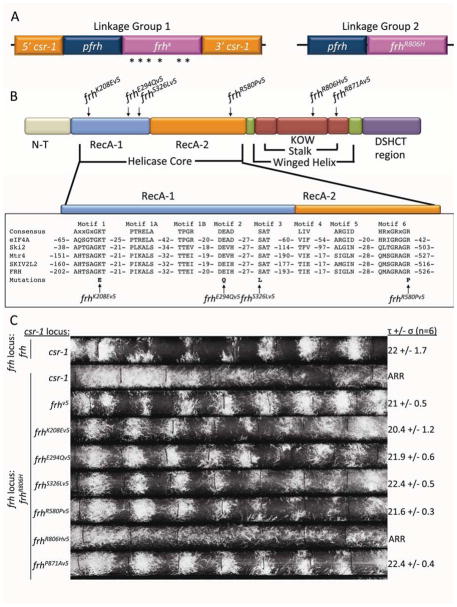
Helicase/ATPase activity is not required for the circadian oscillator-specific function of FRH. (A) Strain genotypes: Linkage group 1; at the csr-1 locus: mutant versions of frh driven by the frh promoter. Linkage group 2; at the frh native locus: frhR806H driven by its native promoter. (B) Colored blocks represent the basic structural domains of FRH as predicted from homology with Mtr4p (Jackson et al., 2010; Weir et al., 2010) as well as the core helicase motifs of eIF4A and other members of the DSHCT helicase family. The location of individual point mutations engineered to cripple the enzymatic functions of FRH are shown schematically at the top and the actual sequence context is provided at the bottom. (C) Race tube assay of wild type (rhythmic, top), frhR806H (arrhythmic, next to last) and the frh mutants knocked into the csr-1 locus (τ = period in hours, σ = standard deviation, n = number of race tubes).