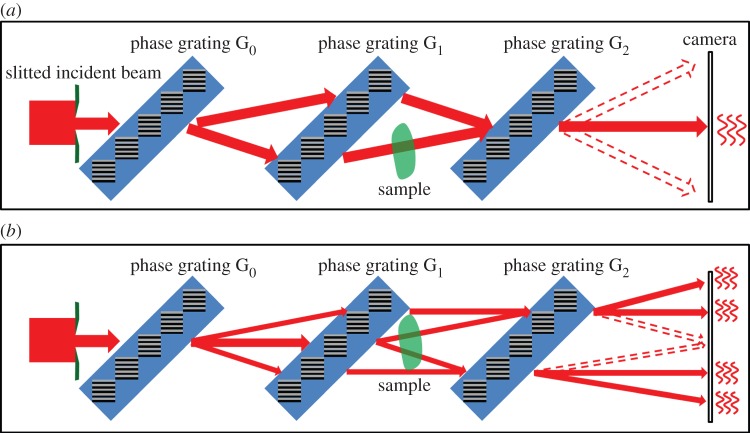
Figure 1.
Two variants of the gBH interferometer. Both consist of a slit that limits the width of the incident beam, followed by three parallel gratings which are positioned in series and at equal spacing, then a gap and the X-ray camera. In variant (a) the first and third diffraction gratings have half the line density as that of the second grating. A pair of balanced diffraction pathways are represented by solid arrows. Other diffracted beams are represented by dotted arrows. Multiple diffraction pathways result in a number of separated diffraction bands on the camera. The pair of balanced paths interfere with each other to produce intensity fringes at the central band. When a sample intersects one or both of the interfering paths, it causes different phase shifts among them resulting in changes of the interference fringes. In variant (b) all three diffraction gratings have the same period. Two pairs of mutually balanced pathways are represented by solid arrows, which results in interference fringes in four diffraction bands on the camera. Variant (b) is realized in our experiment. (Online version in colour.)