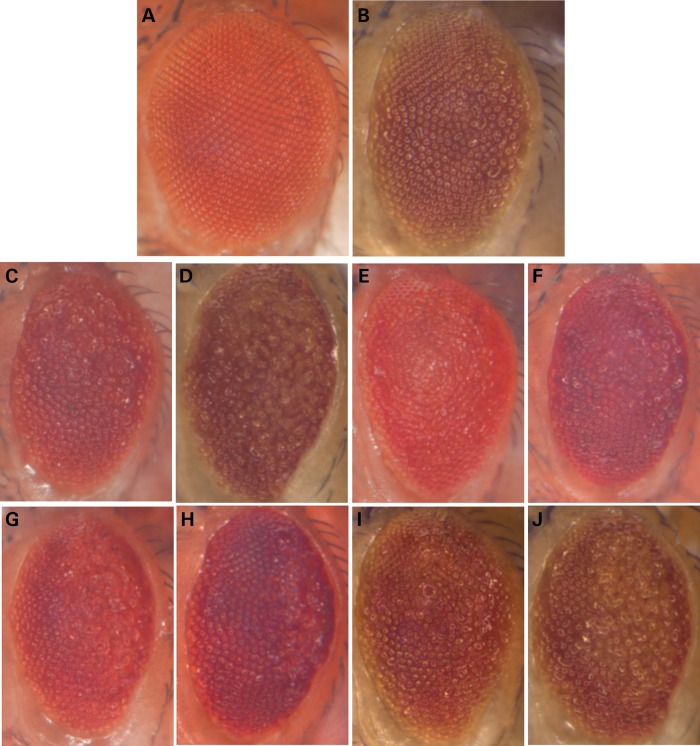
Figure 1.
RNAi-mediated disruption of AD candidate genes enhances Tau toxicity in Drosophila. Compared with control animals (A, GMR-Gal4, UAS-Dcr2/+), expression of human Tau generates a reduced eye size and moderate roughened appearance (B, UAS-TauV337M/+; GMR-Gal4, UAS-Dcr2/+). RNAi directed against several candidate genes enhanced Tau toxicity, exacerbating the rough eye phenotype: oxt (C, UAS-TauV337M/+; GMR-Gal4, UAS-Dcr2/UAS-oxt.RNAi); cindr (D, UAS-TauV337M/+; GMR-Gal4,UAS-Dcr2/+; UAS-cindr.RNAi3.73+81/+); Fit1 (E, UAS-TauV337M/+; GMR-Gal4,UAS-Dcr2/UAS-Fit1.IR.v46495); scb (F, UAS-TauV337M/+; GMR-Gal4, UAS-Dcr2/UAS-scb.IR.JF02696); Lar (G, UAS-TauV337M/UAS-Lar.IR.v36270; GMR-Gal4, UAS-Dcr2/+); SmB (H, UAS-TauV337M/+; GMR-Gal4, UAS-Dcr2/UAS-SmB.IR.HM05097); aret (I, UAS-TauV337M/+; GMR-Gal4,UAS-Dcr2/+; UAS-aret.IR.v41567/+) and CG6498 (J, UAS-TauV337M/+; GMR-Gal4,UAS-Dcr2/UAS-CG6498.IR.v35100). All modifier effects were scored using a semi-quantitative rating scale and found to be significantly different (P < 0.001) from controls, using pairwise independent sample t-tests (Supplementary Material, Fig. S1). The following RNAi lines showed consistent modifier effects, providing further independent confirmation: UAS-cindr.IR.JF02695, UAS-Fit1.IR.v46494, UAS-Lar.IR.HMS00822, UAS-SmB.IR.v110713, UAS-aret.IR.v41568, UAS-CG6498.IR.JF02778 and UAS-CG6948.IR.GL00220. RNAi lines were not associated with any significant toxicity when expressed independently of Tau (Supplementary Material, Fig. S2). RNAi lines used in the screen were obtained from publicly available collections (24,25) or were requested from other Drosophila laboratories (26,44).