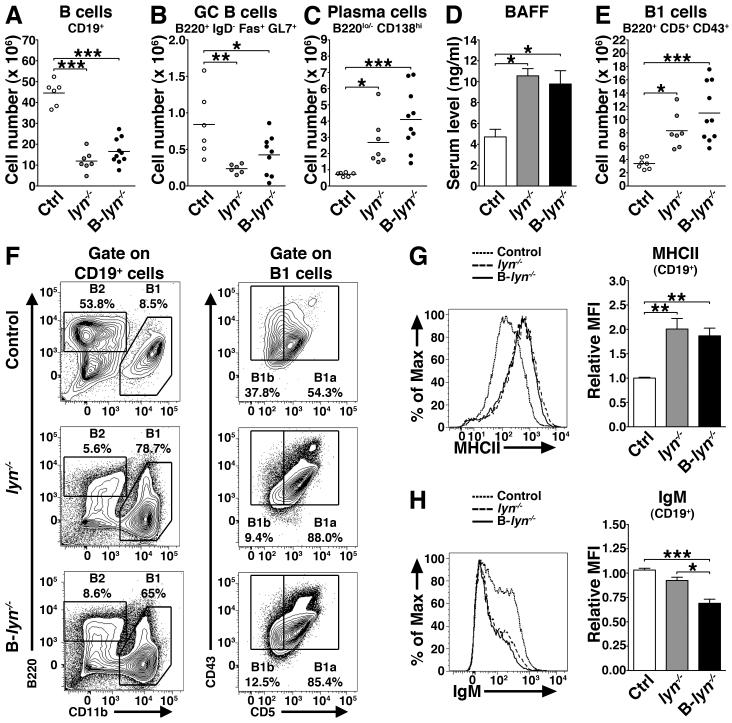
Figure 1. Lyn inhibitory signal in B cells controls B cell homeostasis.
(A-C) Absolute numbers of total B cells (A), GC B cells (B) and plasma cells (C) in the spleens of 8 month-old control, lyn−/− and B-lyn−/− mice. Data represent mean of independent experiments. Each dot represents an individual mouse.
(D) BAFF levels in the serum of control, lyn−/− and B-lyn−/− mice (8 month-old) were determined by ELISA. Bars represent mean ± SEM from 6 – 10 mice per group.
(E) Absolute numbers of B1 cells in the spleens of 8 month-old control, lyn−/− and B-lyn−/− mice. Data represent mean of independent experiments. Each dot represents an individual mouse.
(F) Representative FACS contours showing the percentages of B1 and B2 cells in the peritoneal cavity of 8 month-old control, lyn−/− and B-lyn−/− mice. B1 cells were determined as CD19+ CD11b+ B220lo/− CD43+ cells and further defined as B1a (CD5+) or B1b (CD5−) subsets. B2 cells were determined as CD19+ B220+ CD11b− cells.
(G) Representative FACS histogram showing the expression level of MHCII by splenic B cells from 8 month-old mice (left panel). MFI (Relative to control) of MHCII expressed by B cells in the spleens of 8 month-old mice (right panel). Bars represent mean ± SEM of independent experiments from 6-10 mice per group.
(H) Representative FACS histogram showing the expression level of IgM by splenic B cells from 8 month-old mice (left panel). MFI (relative to control) of IgM expressed by B cells in the spleens of 8 month-old mice (right panel). Bars represent mean ± SEM of independent experiments from 6-10 mice per group.
(A-H) * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001 (One-way ANOVA).