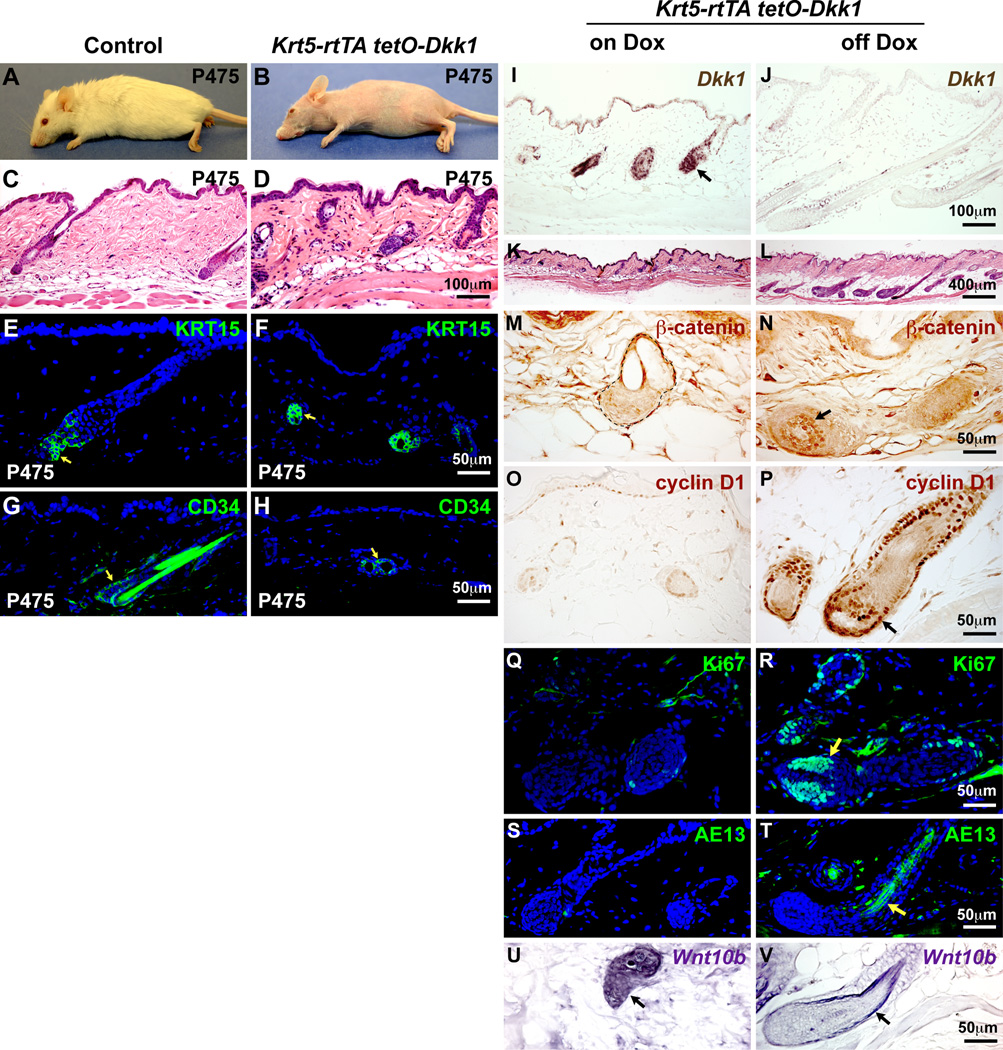
Fig. 6. Dkk1-mediated hair growth inhibition is reversible.
Control and Dkk1 double transgenic mice were induced from P21-P475, and skin biopsies were performed at P475 (on Dox) (A–H,I,K,M,O,Q,S,U) and at P489, 14 days after doxycycline withdrawal (off Dox) (J,L,N,P,R,T,V). Dkk1 transgenic mice completely lacked external hair at P475 (A,B) but HF structures (C,D) and expression of KRT15 (E,F) and CD34 (G,H) (green, arrows) were maintained. (I,J) In situ hybridization reveals Dkk1 expression (brown) in IFE and HFs (arrow) of Dkk1 transgenic skin on Dox (I) and absence of Dkk1 expression following Dox withdrawal (J). (K,L) HFs were arrested in early anagen prior to Dox withdrawal (K) and progressed into full anagen following Dox removal (L). (M–R) Immunostaining reveals absence of nuclear-localized β-catenin (M, brown), cyclin D1 (O, brown), Ki67 (Q, green), and AE13 (S, green) expression in HFs prior to Dox withdrawal, and presence of these markers in HFs following Dox withdrawal (N,P,R,T). (U,V) In situ hybridization for Wnt10b shows its persistent expression (purple) (black arrows) in HFs of Dkk1 transgenic skin on Dox (U) and after Dox withdrawal (V). Arrows indicate positive signals. Scale bars: 400µm (K,L); 100µm (C,D,I,J); 50µm (E–H and M–V). See also Fig. S5.