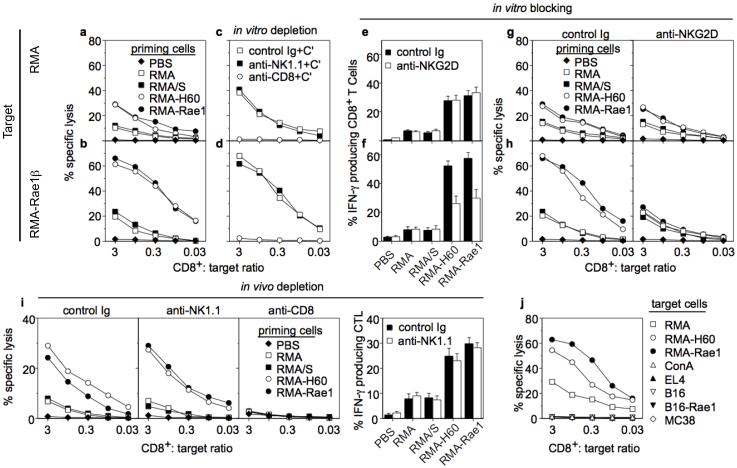
Figure 4.
CTL responses primed by irradiated ligand-transduced RMA cells. Mice were vaccinated with 5×106 irradiated RMA transductants or PBS. Two weeks later splenocytes were restimulated with irradiated RMA-Rae1β cells. a, Lysis of RMA cells. b, Target cell expression of Rae1 resulted in enhanced CTL lysis. c, d, Complement mediated-depletion of CD8 cells but not NK cells abrogates activity of effector cells from RMA-Rae1β vaccinated mice. e, Elevated percentage of RMA-specific IFN-γ producing effector CD8+ CD3+ T cells in mice primed with ligand-transduced RMA cells. Priming cells indicated at bottom. f, Expression of Rae1 by target cells enhances IFN-γ response. The enhancement was completely blocked by anti-NKG2D antibody. g, h, Enhanced lysis of target cells expressing Rae1β is blocked by anti-NKG2D antibody. i, CTL priming occurs in the absence of NK cells. Mice were depleted of NK1.1+ or CD8+ cells prior to and during vaccination with tumor cell transductants. Effector cells were tested for lytic activity and IFN-γ production versus RMA target cells. j, CTL from RMA-Rae1β vaccinated mice specifically recognize RMA cells and remain tolerant of syngeneic T cell blasts. Effector cells from RMA-Rae1β vaccinated mice were tested for lysis of the indicated tumor cells as well as Con A blasts from syngeneic mice. Data are representative of three experiments.