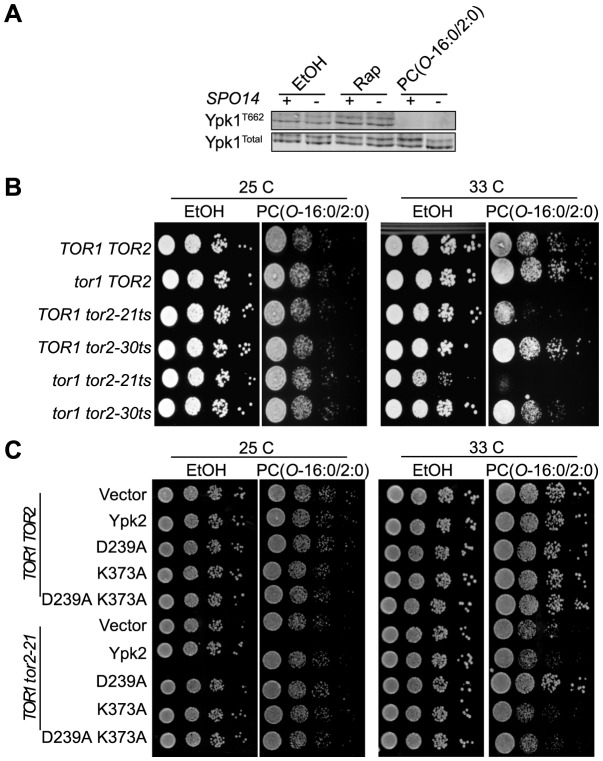
Figure 5. PC(O-16:0/2:0) inhibits TORC2 signaling.
(A) Phosphorylation of the TORC2 substrate Ypk1 is reduced following treatment. TORC2-dependent Ypk1 (T662) phosphorylation status was assessed in whole cell extracts from vehicle (ethanol, EtOH), PC(O-16:0/2:0) (20 µM) or rapamycin (Rap, 200 ng/ml) treated wild type (YPH500) and spo14Δ (YKB2076) cells. Immunoblots were also probed with anti-sera for total Ypk1 to ensure equal loading. (B) tor2-21 mutants display increased sensitivity to PC( O -16:0/2:0). Strains expressing plasmid borne wild type TOR2 or the temperature sensitive (ts) alleles tor2-21 or tor2-30 in a tor1Δ, tor2Δ or a combined tor1Δ tor2Δ background were plated in 10-fold serial dilutions on YPD plates containing vehicle (EtOH) or PC(O-16:0/2:0) (3 µg/ml). Plates were incubated for 2 days at a permissive (25 C) or semi-permissive temperature (33 C). (C) Overexpression of hyperactive Ypk2 suppresses sensitivity to PC( O -16:0/2:0). Ypk2 wild type (Ypk2), hyperactive (D239A), kinase dead (K373A) and the double mutant (D239A and K373A) were transformed into wild type (SH100) and tor2-21 (SH121) expressing cells. Growth was assessed following 2 days at permissive (25 C) and semi-permissive temperature (33 C) on plates containing vehicle (EtOH) or PC(O-16:0/2:0) (3 µg/ml).