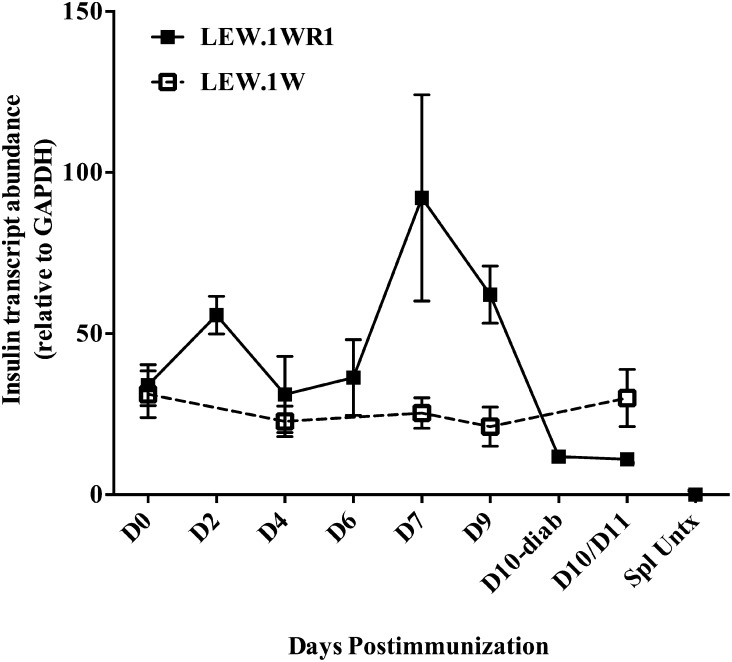
Figure 5.
Altered β-cell function in LEW.1WR1 rats follows Vβ13-specific autoimmunity and is concurrent with significant islet T-cell infiltration. To analyze β-cell dysfunction in the prediabetic islet, we analyzed insulin transcript abundance from poly I:C–treated LEW.1WR1 (susceptible) and LEW.1W (resistant) islets. Insulin transcripts were normalized to GAPDH and the mean ± SE are displayed. LEW.1WR1 islets show significantly elevated insulin transcripts on days 7 and 9 (P = 0.02 and P = 0.01, respectively, vs. untreated), which is severely diminished in the diabetic islet, compared with naïve, day 2, day 7, or day 9 after poly I:C induction (P = 0.001, P < 0.001, P = 0.046, and P = 0.002, respectively). LEW.1W insulin levels do not vary during the course of poly I:C treatment. One of five LEW.1W day 11 islet samples was an outlier (∼2× SD) and was excluded from the above data set, but may be biologically relevant given that 1) a small proportion of LEW.1W rats become diabetic with poly I:C treatment and 2) Vβ13+ T cells begin to accumulate in the islets of some LEW.1W rats on days 9–11. Spleen samples from untreated LEW.1WR1 rats were analyzed as a negative control for insulin transcript production. N = 3–5 rats per time point, 29 LEW.1WR1, 18 LEW.1W total. D, day; diab, diabetes; Spl Untrx, untreated spleen.