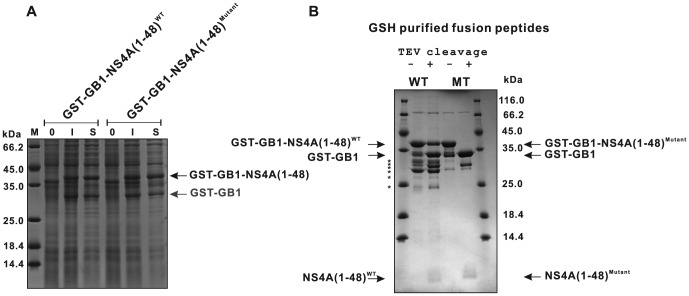
Figure 4. Expression of NS4A(1–48) wild type and mutant peptides using a dual GST-GB1 tag.
(A) Relative expression levels of GST-GB1-NS4A(1–48) and the GST-GB1-NS4A(1–48; L6E, M10E) mutant were analyzed by SDS-PAGE using aliquots of the expression cultures. Shown are samples obtained from culture at 0 (0) or 3 hours (I) following IPTG induction or the supernatant after cell lysis (S). (B) TEV digest of GST-GB1-NS4A(1–48) wild type and mutant protein fusions. Aliquots of GSH-purified supernatants of wild type and mutant fusion proteins before and after TEV cleavage are shown. Note that besides the GST-GB1-NS4A(1–48) full-length product also shorter fragments, likely GST-GB1 and other truncation fragments, marked by asterisks were produced, which are present in the GSH-purified samples already prior to TEV cleavage. Because staining of free NS4A(1–48) peptides is very faint under the conditions used, the progress of the TEV digest is monitored by observing the decrease of the band for the dual tagged GST-GB1-NS4A(1-48) fusion protein in parallel with an increase of the band for the free GST-GB1 dual tag. A densitometric analysis of the respective bands revealed a cleavage efficiency of approximately 50% for the wild type peptide.