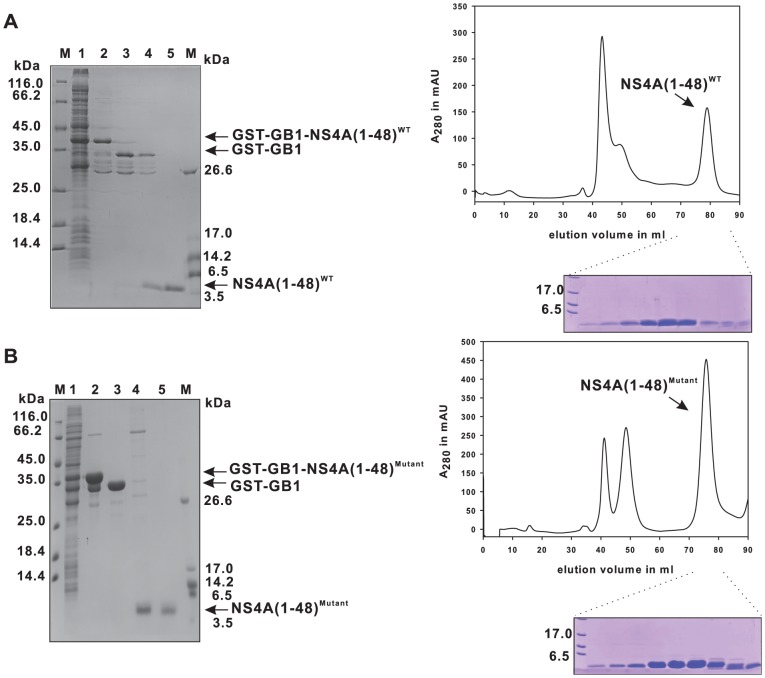
Figure 6. Purification of recombinant NS4A(1–48) wild type and mutant peptides.
The 15% SDS-PAGE gel containing samples from various steps in the purification procedure is shown on the left. The wild type peptide is shown in (A) while the mutant is shown in (B). The supernatant after cell lysis is shown in lane 1. The lysate containing the peptide was loaded on a GSH sepharose column (lane 2), and cleaved by TEV protease on the column, the cleaved protein is shown in lane 3. The GSTfusion tag remained bound to the column, while the NS4A(1–48) peptide was collected from the flow-through (lane 4). The peptide was further purified by size exclusion chromatography (lane 5). The mutant peptide was purified using the same strategy (B). The respective size exclusion chromatography profiles (HiLoad 16/60 Superdex 75 prep grade) of the flow-through fraction from the TEV protease on column cleavage step - mainly containing TEV protease and NS4A(1–48; L6E, M10E) or NS4A(1–48) peptides - are shown on the right with the matching SDS-PAGE analysis of the NS4A containing fractions.