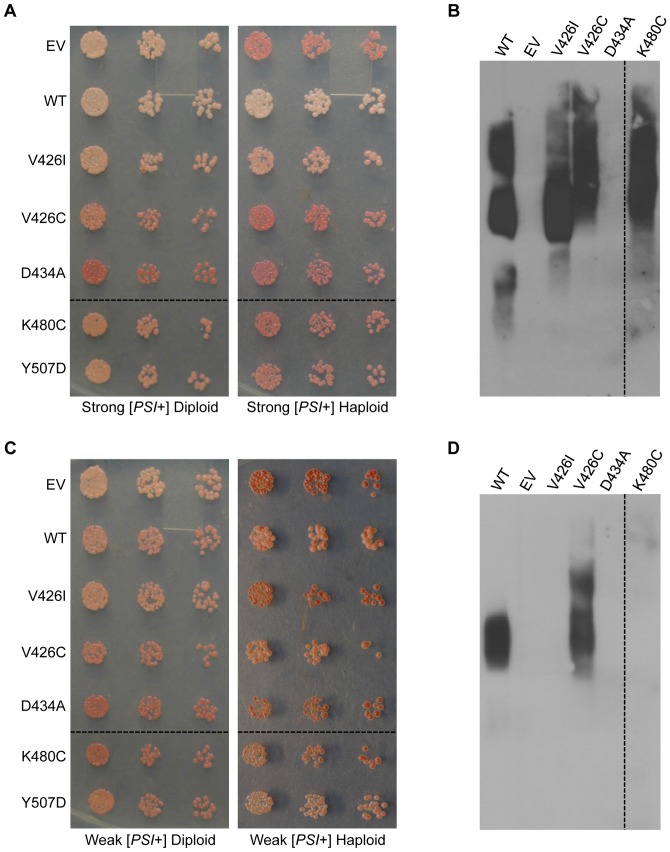
Figure 6. M-domain mutants differentially affect propagation of strong and weak variants of [PSI+].
(A) Heterozygous HSP104/hsp104Δ diploids or hsp104Δ haploids propagating strong [PSI+] and containing plasmids expressing HSP104 (WT), hsp104-V426I, hsp104-V426C, hsp104-D434A, hsp104-K480C, hsp104-Y507D, or an empty vector control (EV), were normalized, serially diluted five-fold, and spotted on medium to select for the plasmid. Dashed lines represent different parts of the same plate that have been cropped for clarity. (B) Strong [PSI+] hsp104Δ haploids harboring the indicated Hsp104 plasmid or containing an empty vector control (EV) were subjected to SDD-AGE and western blot with an antibody against Sup35. The dashed line represents different parts of the same gel that have been cropped for clarity. This is one representative of three separate experiments. (C) Heterozygous HSP104/hsp104Δ diploids or hsp104Δ haploids propagating weak [PSI+] and containing plasmids expressing HSP104 (WT), hsp104-V426I, hsp104-V426C, hsp104-D434A, hsp104-K480C, hsp104-Y507D, or an empty vector control (EV), were normalized, serially diluted five-fold, and spotted on medium selecting for the plasmid. Dashed lines represent different parts of the same plate that have been cropped for clarity. (D) The weak [PSI+] parental strain (WT) and weak [PSI+] haploids harboring the indicated Hsp104 plasmid or an empty vector control (EV) were subjected to SDD-AGE and western blot with an antibody against Sup35. The dashed line represents different parts of the same gel that have been cropped for clarity. This is one representative of five separate experiments.