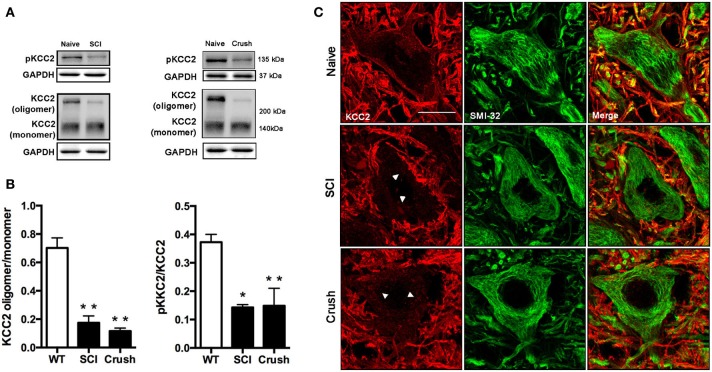
Figure 4.
Analysis of KCC2 and phopho-KCC2 expression in the ventral spinal cord of SCI and sciatic nerve injured mice. (A) Representative blots of phopho-KCC2 and total KCC2 (on both monomeric and oligomeric states) in SCI and crush mice. (B) KCC2 western blots quantifications. Graphs represent the ratio between the oligomeric KCC2 (functional state) vs. monomeric KCC2 and the phopho-KCC2 (active form) vs. monomeric KCC2. Both analyses revealed a decrease in the active form of the KCC2 in SCI (28 days after injury) and in sciatic nerve crush (7 days after injury). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m.; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. naïve animals. (C) Confocal images of L4 spinal MNs revealed the presence of membrane-bound (active) KCC2 in naïve but not in SCI and sciatic nerve injured animals. Arrowheads point internalized KCC2 aggregates. Scale bar 20 μm.