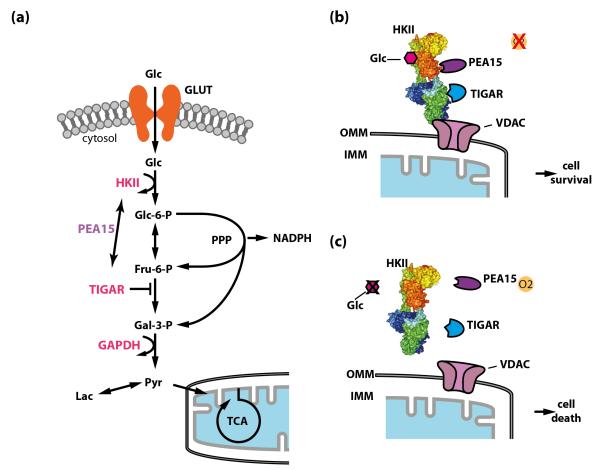
Figure 3. The connection between glucose metabolism and cell death.
(a) Glucose metabolism and cell death regulation intersect at several levels. Glucose metabolizing enzymes, including hexokinase II (HKII), glucokinase (GK), the fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase TIGAR (Tp53-induced Glycolysis and Apoptosis Regulator), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and others, are involved in the regulation of cell death through different mechanisms. Phosphoprotein-enriched in astrocytes (PEA15) might function as a molecular linker between HKII and TIGAR under certain conditions. Flux through the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) generates NADPH, which is important for neuronal redox environment and inhibits cell death. (b) and (c) The expression of HKII in neurons is upregulated under hypoxic conditions. Together with PEA15 it functions as a molecular switch to regulate neuronal viability depending on the metabolic state [72]. HKII and PEA15 interact and bind to mitochondria through the outer-mitochondrial membrane voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC). During hypoxia, HKII protects cells from cell death, whereas during glucose deprivation, where HKII detaches from mitochondria and the interaction with PEA15 is destabilized, HKII promotes cell death [72]. HKII also interacts with TIGAR under hypoxic conditions [77]. Similar to PEA15, which increases the capacity of HKII to protect neurons, TIGAR increases the glycolytic activity of HKII. However, the exact mechanistic link is presently unknown. Glc, glucose; GLUT, glucose transporter; Glc-6-P, glucose-6-phosphate; Fru-6-P, fructose-6-phosphate; Gal-3-P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; Lac, lactate; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; Pyr, pyruvate; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane. HKII was rendered in Pymol using structure 2nzt (RCSB Protein Data Bank).