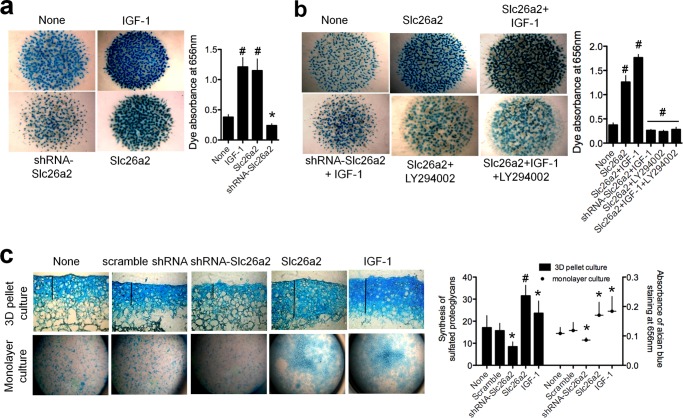
FIGURE 4.
Slc26a2 is essential for proteoglycan synthesis by chondrocytes. a and b, micromass cultures of embryonic limb mesenchymal cells were prepared from limb buds of E11.5 embryos and allowed to undergo condensation to form cartilaginous nodules consisting of sulfated proteoglycans. Infection with lentiviruses carrying Slc26a2 and shSlc26a2 were as described under “Materials and Methods.” The cultures were treated with vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide), 10 μm of the PI3K inhibitor LY29002, or 100 ng/ml IGF-1. At the end of the incubation, the micromasses were stained with Alcian blue to visualize the sulfated proteoglycans. In a, the controls are micromasses without any treatment. In b, the controls are micromasses treated with dimethyl sulfoxide. The results are representative of three to four experiments, and the columns show the mean ± S.E. c, three-dimensional (3D) cultures (n = 4–5) and a monolayer culture (n = 3) of mouse articular chondrocytes were prepared as detailed under “Materials and Methods,” infected with Slc26a2 or shSlc26a2, and treated with 100 ng/ml IGF-1. The controls were cultures without any treatment. After 5 days in culture, sulfated proteoglycans were analyzed by staining with Alcian blue and measurements of the Alcian blue absorbance. Shown are representative images, and the columns are mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05; #, p < 0.01 relative to the respective untreated controls (None).