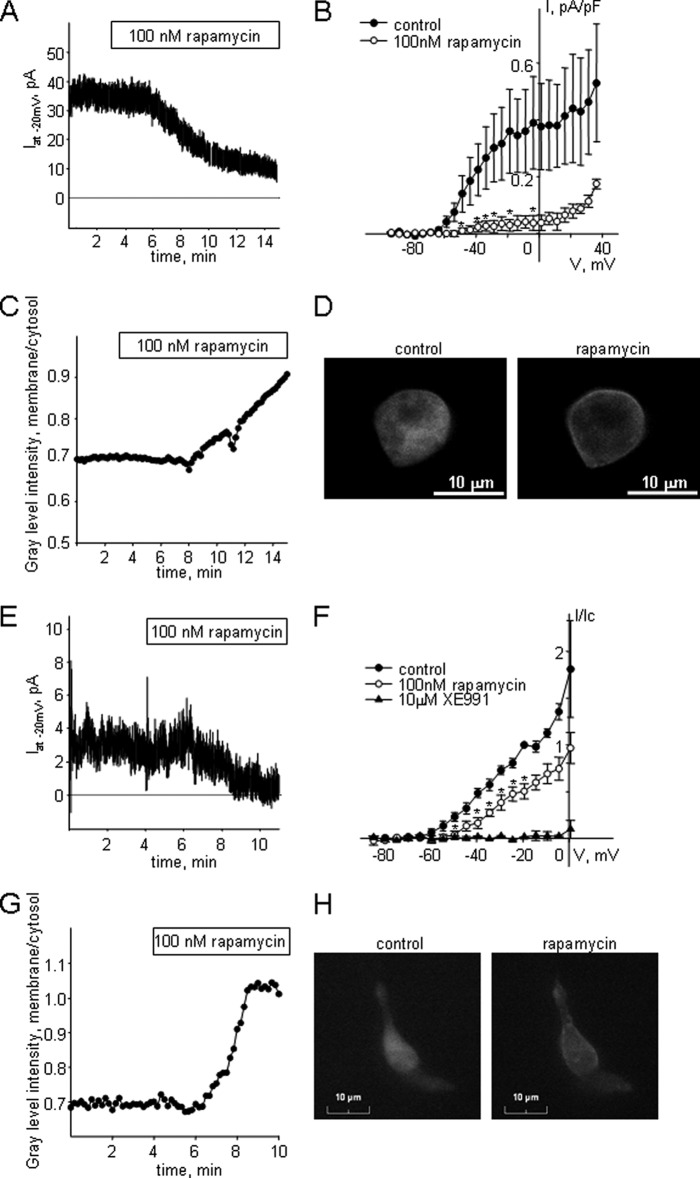
FIGURE 4.
Suppression of endogenous Kv7 currents in A7r5 cells and MASMCs upon activation of PKCα using a rapamycin-induced PKCα translocation system. A, representative time course of Kv7 current inhibition in an A7r5 cell upon application of rapamycin (100 nm). B, mean I-V curves of steady-state Kv7 currents recorded in A7r5 cells with a voltage step protocol before (control, filled circles) and after treatment with 100 nm rapamycin for 12 min (open circles) (n = 3). C, representative time course of PKCα translocation recorded simultaneously with current inhibition presented on panel A in an A7r5 cell upon application of rapamycin (100 nm). D, representative images of an A7r5 cell used for recordings for panels A and C before application of rapamycin (100 nm, left panel) and at the end of application of rapamycin for 12 min (right panel). E, representative time course of Kv7 current inhibition in a MASMC upon application of rapamycin (100 nm). F, mean I-V curves of steady-state Kv7 currents recorded in MASMCs with a voltage step protocol before (control, filled circles), after treatment with 100 nm rapamycin for 12 min (open circles) and after treatment with 10 μm XE991 (filled triangles). Currents were normalized by the current recorded at −20 mV before application of rapamycin. *, significant difference from control, p < 0.05, Student's paired t test, n = 4). G, representative time course of PKCα translocation recorded in an MASMC upon application of rapamycin (100 nm). H, representative images of the MASMC used for recordings for panel G before application of rapamycin (100 nm, left panel) and at the end of application of rapamycin for 10 min (right panel).