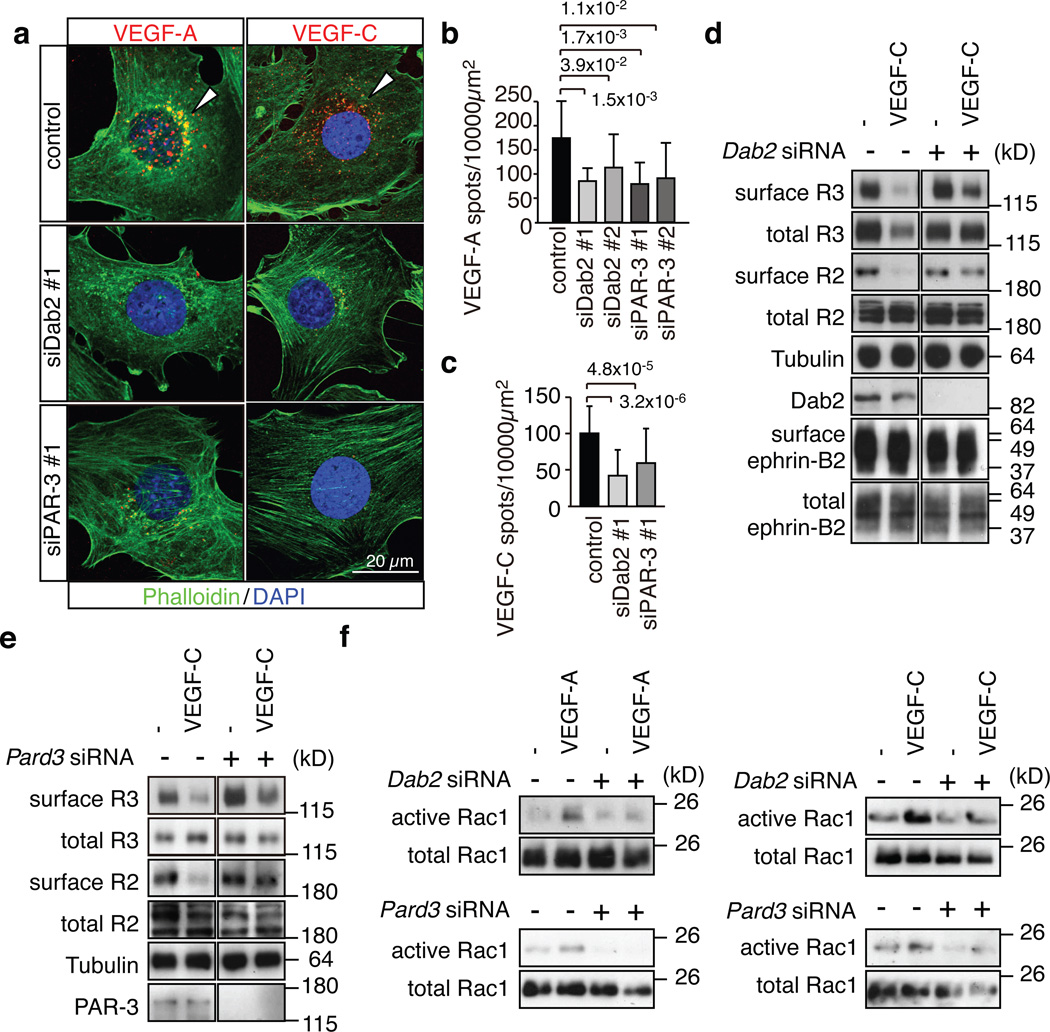
Figure 4. Dab2 and PAR-3 control VEGF receptor internalisation.
a, Alexa546-labelled VEGF-A or VEGF-C (red) accumulated in the perinuclear region of control mouse ECs at 30 min after stimulation, which was strongly reduced after knockdown of Dab2 or Pard3. Actin, Phalloidin (green); nuclei, DAPI (blue).
b, c, Quantitation of Alexa546-positive peri-nuclear VEGF-A (b) or VEGF-C (c) spots. Two different siRNAs were used for Dab2 and Pard3 in (b). Data represent the means±s.d. of 6 independent experiments. P values, two-tailed Student’s t-test. At least 100 cells were scored in each experiment.
d, e, Biochemical detection of biotinylated (surface) VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 in stimulated control and Dab2 (d) or Pard3 (e) KD cells. Antibodies used for immunoblotting and molecular weight marker are indicated.
f, Activation of Rac1 in control and Dab2 or Pard3 KD mouse ECs stimulated with VEGF-A or VEGF-C for 5 min, as indicated.