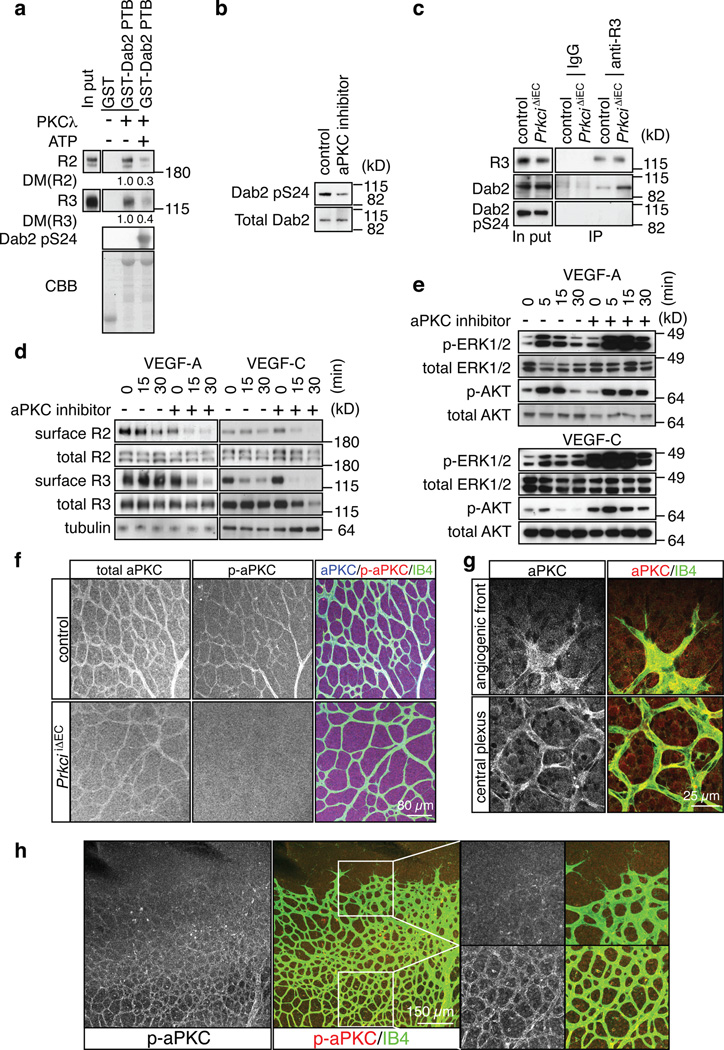
Figure 6. Negative regulation of VEGF receptor internalisation by aPKC.
a, Phosphorylation of a GST-Dab2 fusion protein by recombinant PKCλ reduced its interaction with VEGFR3 and VEGFR2 in pull down assays. Densiometric (DM) values are shown below bands. ATP for the kinase activation was added (+) or absent (−), as indicated. CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining of GST fusion proteins.
b, Western blot showing reduced Dab2 phoshorylation at Serine 24 (pS24) in cultured ECs after 30 min incubation with 5µM aPKC inhibitor.
c, Association of Dab2 with immunoprecipitated VEGFR3 (anti-R3) was enhanced in PrkciiΔEC lung lysate compared to control littermates. No specific bands were immunoprecipitated with IgG. VEGFR3-associated Dab2 lacked detectable phosphorylation in Ser24 (pS24).
d, Effect of aPKC inhibition on VEGF-A- or VEGF-C-induced VEGF receptor internalisation at indicated time points. Cells were preincubated with 5 µM of aPKC inhibitor for 30 min. Surface VEGFR2 (R2) and VEGFR3 (R3) were identified by biotinylation.
e, Increased activation of MAP kinase (p-ERK1/2) by VEGF-A or VEGF-C after aPKC inhibition in cultured mouse ECs. Effects on AKT phosphorylation were comparably modest. Total ERK1/2 and AKT are shown as loading controls. Molecular weight marker (kD) is indicated.
f, Anti-aPKC (total), anti-phospho-aPKC (p-aPKC, Thr560) and Isolectin B4 (IB4) staining of the P6 control and PrkciiΔEC retinal vasculature.
g, Anti-aPKC immunostaining (red) labels ECs (IB4, green) at the angiogenic front and in the central retinal plexus.
h, Phospho-aPKC (p-aPKC, Thr560) immunosignals were weak at the angiogenic front in comparison to vessels of the central plexus. Higher magnification of p-aPKC signals and merged channels in insets is shown on the right.