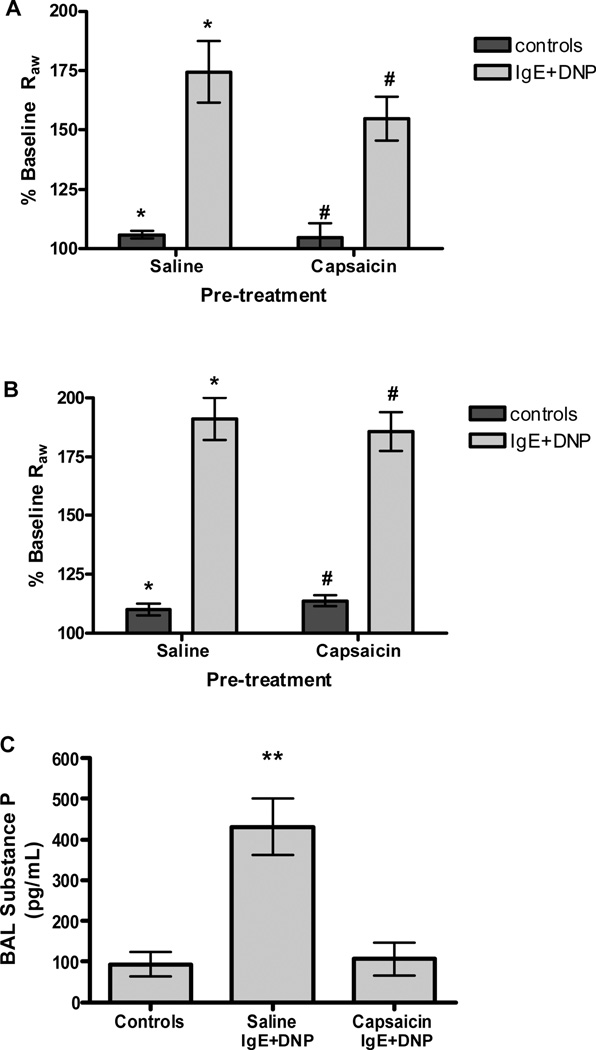
Figure 4. Anaphylactic bronchoconstriction following ablation of sensory C-fibers with capsaicin.
(A) Sensory ablation with capsaicin (25–75 mg/kg) in adults (n=6) had no significant effect on airway constriction after antigen challenge in passively sensitized mice (*P<0.001, #P<0.01). (B) Degradation of C-fibers with capsaicin (50 mg/kg) in newborn mice (n=7) had no effect on airway parameters after antigen challenge in passively sensitized mice (*P<0.001, #P<0.001). (C) Antigen challenge in passively sensitized mice (n=10) increased substance P content in the BAL. Neonatal treatment of capsaicin (n=5) reduced BAL substance P after antigen challenge to levels seen in control animals (n=3) (**P<0.05, compared to all other groups).