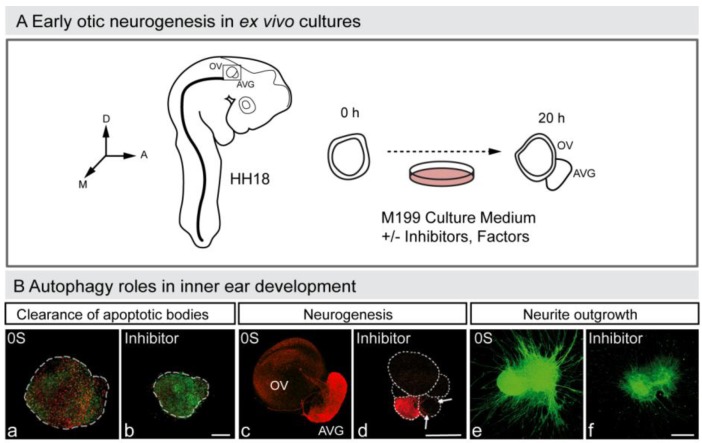
Figure 3.
Autophagy in early otic neurogenesis. (A) Schematic representation of the otic vesicle ex vivo culture. The otic vesicle can be explanted from the embryo at HH18. The acoustic-vestibular ganglion also develops ex vivo, and thus this constitutes an excellent model to study otic neurogenesis. The figure shows a schematic drawing of a HH18 chicken embryo showing the location of the otic vesicle, of an otic vesicle immediately after dissection (0 h) and after 20 h in culture (20 h). Factors and drugs can be added to the serum-free culture medium to study their effects on the otic vesicle’s ex vivo development and AVG formation. Abbreviations: AVG, acoustic-vestibular ganglion; OV, otic vesicle. (B) Autophagy and inner ear development. Otic vesicles were incubated with or without autophagy inhibitor and then labeled to detect apoptotic cells with annexin-V (An-V, red) and TUNEL (green) (a,b), or to study neurogenesis (red; c,d). The AVG can also be cultured and labeled to study axon outgrowth (green; e,f). Orientation: A, anterior; D, dorsal; M, medial. (Adapted from [88]).