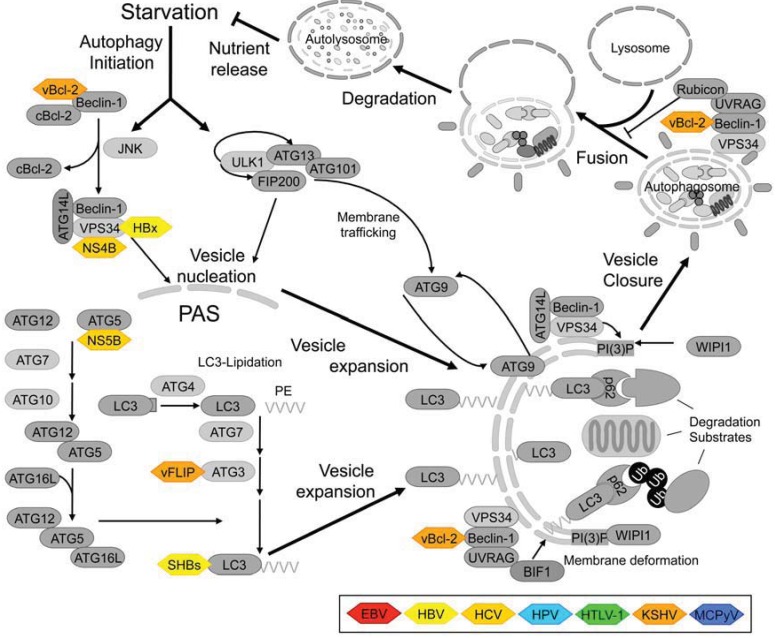
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the autophagy pathway in mammalian cells and interactions with viral proteins.
The Atg-proteins can be grouped into four (or into six, according to other authors, e.g., [116]) functional modules that mediate the major steps of autophagy [117]: (1) An autophagy initiation complex consisting of the Serine/Threonine kinase ULK1 (or its close relative ULK2), and the regulatory proteins ATG13, focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200 kD (FIP200) and ATG101 [116]; (2) A class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), VPS34, which, in cooperation with its interaction partners, facilitates vesicle nucleation. There are at least three biochemically and functionally distinct class III PI3K-complexes in mammalian cells, which share a common core comprising VPS34 itself and ATG6/Beclin-1 as well as p150 and Ambra-1 (omitted for clarity). The first complex comprises the core and ATG14L/Barkor and mediates autophagosome nucleation. The second complex, containing the core and UV irradiation resistance associated protein (UVRAG) may be involved in autophagosome extension and/or other endosomal pathways [118]. The third complex, in which the core is associated with UVRAG and RUN domain and cysteine-rich domain containing Beclin-1 interacting protein (Rubicon) inhibits autophagosome and endosome maturation; (3) Two interconnected ubiquitin-like conjugation systems involved in autophagosome expansion and cargo recruitment. In these systems, the E1- and E2-like enzymes, ATG7 and ATG10, respectively, facilitate conjugation of the ubiquitin-like protein ATG12 to ATG5. This ATG5-ATG12 conjugate is localized to the expanding autophagosomal membrane by ATG16L and potentially serves as the E3-ligase in the second conjugation system, which facilitates lipidation of the peripheral membrane protein LC3. Conjugation of LC3 further requires proteolytic processing by ATG4, as well as the E1-like enzyme ATG7 and another E2-like enzyme, ATG3 [117]. (4) A membrane trafficking and recycling system whose components are still poorly characterized functionally and include WD repeat domain phosphoinositide-interacting protein 1 (WIPI1), which binds phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (the product of the VPS34-lipid kinase reaction) and the putative membrane carrier protein ATG9 as well as another transmembrane protein, VMP1, and ATG2 (omitted for clarity) [117]. Some substrates are marked for autophagic degradation by ubiquitination, and both ubiquitinated and non-ubiquitinated cargo can be recruited to the autophagosome by LC3‑interacting adaptor proteins such as p62/sequestosome 1 [119]. Autophagic adaptors are especially important in selective forms autophagy and may also play a role in xenophagy of viral proteins [120]. Viral proteins that have been reported to physically interact with components of the autophagy machinery are depicted in this schematic drawing. Please note that upstream signaling pathways that target the ULK1-autophagy initiation complex or one of the other Atg-proteins and viral proteins interfering with them were omitted from this figure for clarity but are shown in detail in Figures 3-5. Some of the interactions of viral proteins with host cell autophagy-factors may require further experimental validation (see main text). Light grey rounded rectangles-host cell proteins with enzymatic activity; dark grey rounded rectangles-other host cell proteins; colored hexagons-viral proteins; : activation; to ⊥: inhibition.