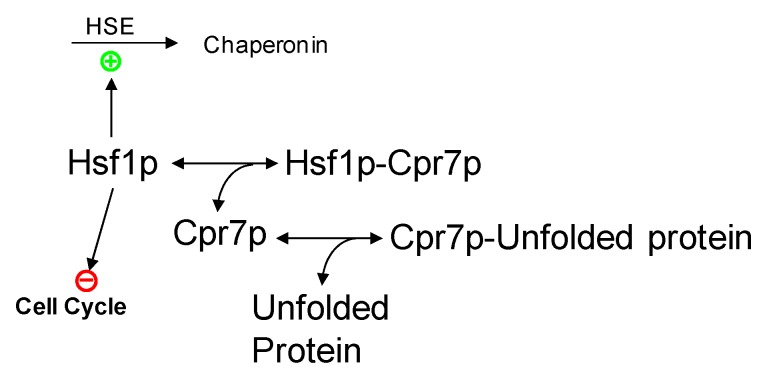
Figure 1.
Modeling heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) activation. Free HSF1 protein binds to the heat shock element (HSE) and helps elicit the heat shock response, by inhibiting cell cycle progression and leading to the expression of chaperonins. In the absence of heat-unfolded proteins, the HSF1 protein is kept inactive by the CPR7 protein (Hsf1p-Cpr7p). Under heat stress, the CPR7 protein is sequestered by heat-unfolded proteins, thus releasing its inhibitory effect of HSF1.