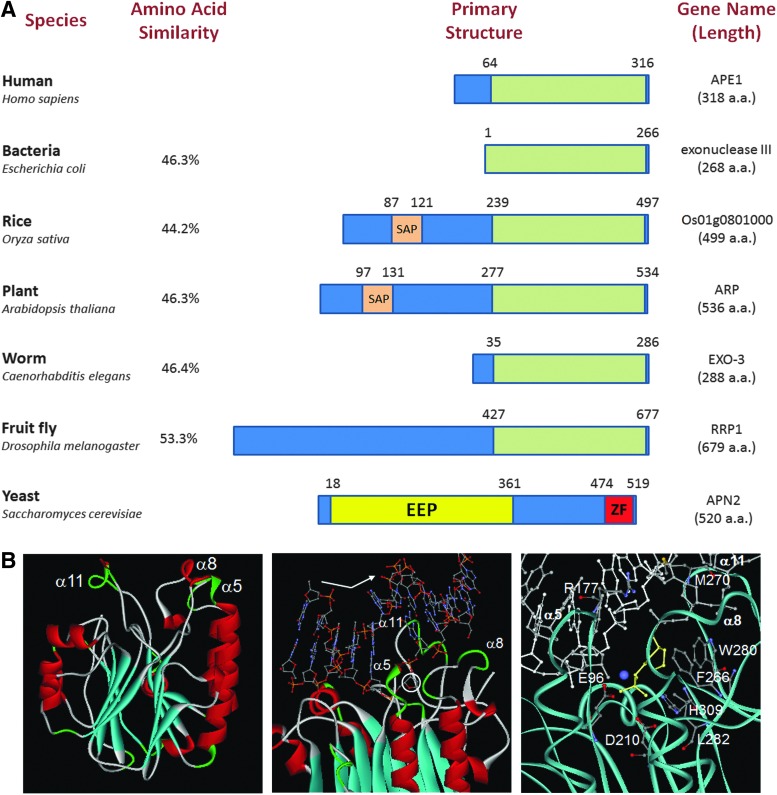
FIG. 3.
Human APE1 orthologs and key protein structural elements. (A) APE1 orthologs. The particular species (left) and gene name (right) are indicated. Shown is the primary structure, with the AP endonuclease domain designated as a green box. Total amino-acid sequence length and percent similarity with human APE1 are specified. SAP, SAF-A/B, Acinus and PIAS motif, which is a putative DNA/RNA binding domain; EEP, Exonuclease-Endonuclease-Phosphatase domain; ZF, zinc finger. (B) APE1 structural features. All images were created using the DS ViewerPro software (Accelrys, San Diego, CA). Left: ribbon diagram of human APE1 [coordinates from 1BIX (63)]. The major recognition loops are designated. Middle: diagram of APE1 bound to un-incised AP-DNA [coordinates from 1DE8 (145)]. Recognition loops are indicated, and the abasic site is circled. Note the 35° kinking of the DNA backbone (emphasized by arrow). Right: diagram of the binding surface and active site of APE1 in complex with incised AP-DNA and Mn2+ [coordinates from 1DE9 (145)]. DNA strands are shown in white, with the 5′-abasic residue designated in yellow. The protein is shown as a cyan ribbon. The recognition pocket (comprising F266, W280, and L282) and several key active site residues (E96, D210, and H309) are highlighted. The recognition loops, and two key binding residues (R177 and M270), are also indicated. The catalytic metal ion is depicted as a purple sphere. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars