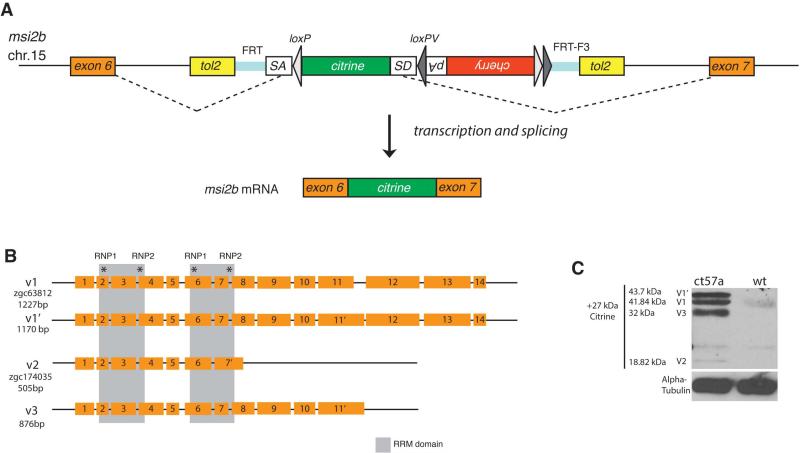
Figure 1. A novel gene trap line depicts expression of Msi2b in zebrafish.
(A) Schematic diagram of the FlipTrap strategy. The FlipTrap construct contains an artificial exon consisting of citrine ORF sequence lacking start and stop codons (green), flanked by rassf8 splice acceptor (SA) and donor (SD) sites. Genomic integration of the construct is mediated by Tol2 transposase. In the gt(msi2b-citrine)ct57a line, the FlipTrap construct has inserted in the chromosome 15, within the intron between exons 6 and 7 of msi2b. The endogenous splicing machinery recognizes the splice acceptor (SA) and splice donor (SD) sites flanking the citrine sequence (dashed lines), resulting in Citrine-fusion with endogenous protein.
(B) Schematic diagram of zebrafish msi2b splice variants. Members of the Msi family of RNA-binding proteins are characterized by the presence of two RNA-binding domains (gray boxes) that include two short highly conserved motifs called RNP-1 and RNP-2 (asterisks). Alternative splicing of msi2b produces 3 splice variants (v1, v2, v3).
(C) Detection of Msi2b protein fused with Citrine-tag reveals Msi2b the presence and relative abundance of variants at the protein level. Expression of Msi2b variants by western blot in gt(msi2b-citrine)ct57a embryos at 56 hpf. Alpha-Tubulin is used as a load control.