Figure 1.
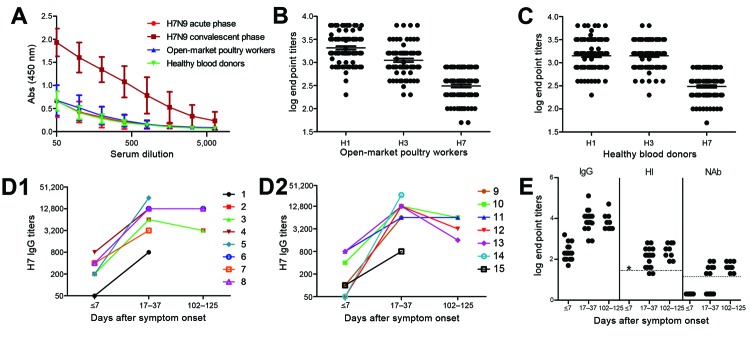
Serum antibodies (Abs) in patients infected with influenza A(H7N9) virus and in control populations (poultry-market workers and healthy blood donors), China, 2013. A) Dilution curves of IgG against subtype H7 in serum samples. Bars indicate SE. B and C) Titers of IgG against H7, H1, and H3 in poultry-market workers (B) and healthy blood donors (C). D) Increasing titers of IgG against subtype H7 after symptom onset in patients from whom paired serum samples were collected. E) Levels of IgG against H7, neutralizing antibodies (NAbs), and hemagglutination inhibition (HI) in serum samples after symptom onset. IgG against hemagglutinins of H7 and seasonal influenza A viruses (subtypes H1 and H3) in patients with subtype H7N9 virus infection and control populations were titrated by ELISA by using recombinant hemagglutinin antigens. NAbs were assessed by microneutralization assay the influenza A/Anhui/1/2013 (H7N9) strain. HI antibodies (Abs) were assessed by HI assay that used a β-propriolactone–inactivated influenza A/Anhui/1/2013 (H7N9) strain. B–E) Serum IgG, NAb, and HI titers were transformed to log10. For NAb-negative samples, titers of 2 were used for log10 transformation. Serum with titers >40 were considered HI positive for H7-specific antibody. The HI dotted line denotes a titer of log1040 = 1.60. Serum with titers >20 were considered NAb positive for H7-specific antibody. The NAb dotted line denotes a titer of log1020 = 1.30. *, not available.
