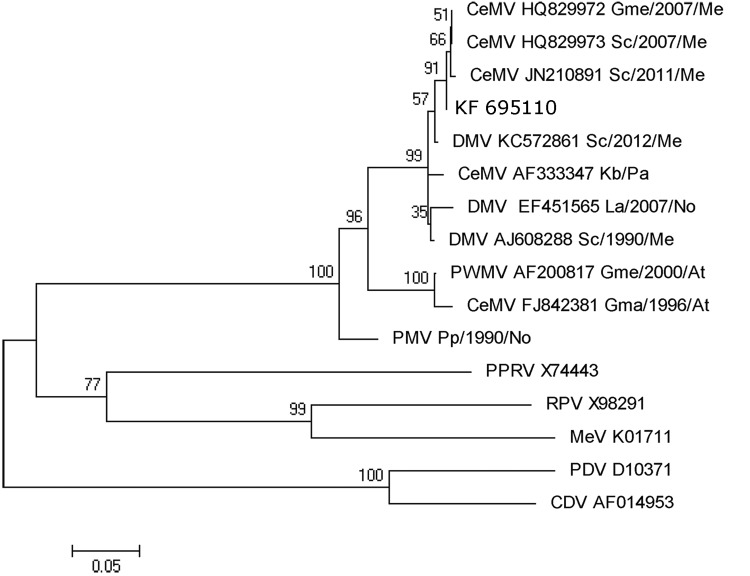
Figure 2.
Phylogram of morbillivirus phosphoprotein gene sequences. MEGA 5.0 software (www.megasoftware.net) was used to construct the maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees. A Tamura-Nei substitution model and a bootstrap resampling (1,000 replicates) were used to assess the reliability of the trees. Bootstrapping values are indicated as percentages next to bifurcations. The new isolate from this study has the GenBank accession no. KF695110. Sequence names include the virus name (CeMV, cetacean morbillivirus; DMV, dolphin morbillivirus; PWMV, pilot whale morbillivirus; PMV, porpoise morbillivirus; PPRV, peste-des-petits-ruminants virus; RPV, rinderpest virus; MeV, measles virus; PDV, phocine distemper virus; CDV, canine distemper virus; GeneBank accession numbers (when available); cetaceans species (Gme, Globicephala melas; Sc, Stenella coeruleoalba; Kb, Kogia breviceps; La, Lagenorhynchus albirostris; Gma, Globicephala macrorhynchus; Pp, Phocoena phocoena; Tt, Tursiops truncatus); and the year and the geographic area of the stranding (Me, Mediterranean Sea; Pa, Pacific Ocean; No, North Sea; At, Atlantic Ocean. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.