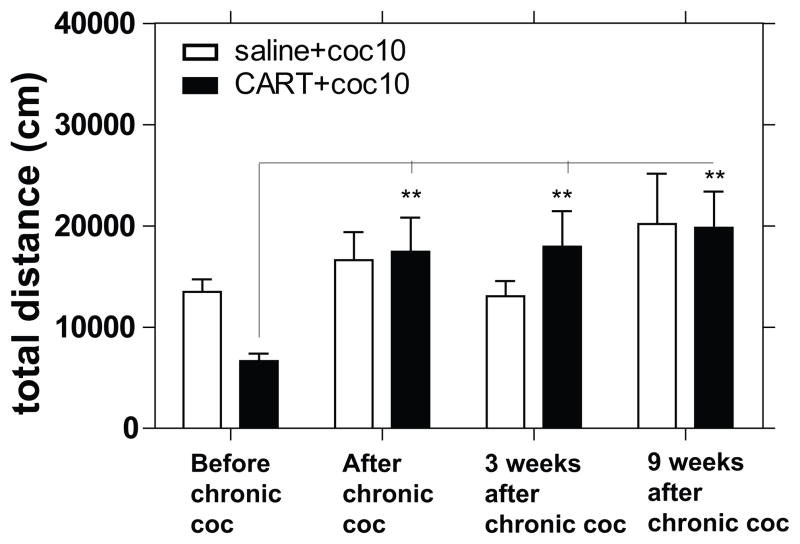
Fig 3. The effect of CART peptide after withdrawal of repeated injections of cocaine.
CART55-102 (2.5 ug) or saline was administered directly into the NAc of male rats immediately before an ip injection of saline or cocaine (coc) (10 mg/kg) acutely (day 1), after additional 13 days (day 14) of cocaine (10 mg/kg) administration once daily and at different time points after withdrawal of chronic administration of cocaine-10 mg/kg and LMA was measured. The groups were as follows (before chronic coc administration) [saline+coc (n = 15), CART+coc (n = 15)], (after chronic coc administration) [saline+coc (n = 13), CART+coc (n = 13)], (3 weeks after chronic coc administration) [saline+coc (n = 10), CART+coc (n = 10)], and (9 weeks after chronic coc administration) [saline+coc (n = 7), CART+coc (n = 8)]. The y-axis represents distance covered in 60 min after cocaine injection. The x-axis represents the conditions relative to chronic coc administration. 2-way ANOVA showed no significant treatment effect (F 1, 83 = 0.03841, P = 0.8451), a significant difference between conditions relative to time before chronic coc (F 3, 83 = 5.199, **P = 0.0024) and no interaction (F 3, 83 = 1.931, P = 0.1309). Bonferroni post hoc tests showed that the effect of CART+coc before chronic coc was significantly different from its effect after chronic coc and even after allowing rat to recover for up to 9 weeks after chronic coc. The p-values *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 show difference when comparing treatment groups between all conditions relative to chronic coc. The significant differences after post hoc analysis are shown on the graph.