Figure 1. The α5 subunit plays an important role for sedative dose of ethanol and influences ethanol-induced ataxia.
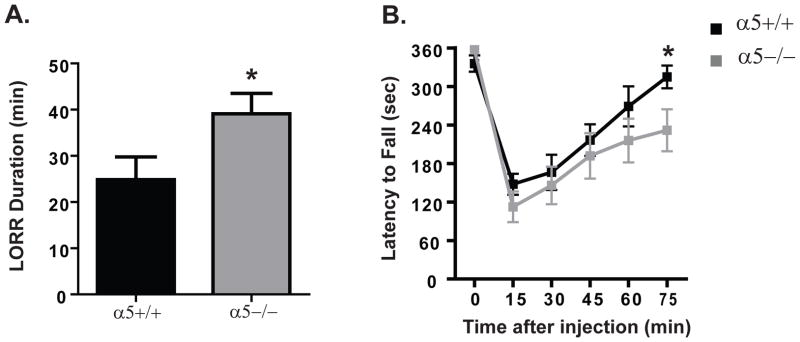
(A) The loss of righting reflex (LORR) duration for 3.2g/kg (i.p.) ethanol was shorter for α5+/+ (black) compared to α5−/− (gray) mice. (B) On the accelerating rotarod, α5−/−(gray) had an increased latency to fall compared to α5+/+ (black) mice for 2 g/kg (i.p.) ethanol dose. In A, n=8–13 animals, B, n=11 animals. The values are expressed as duration (mins) ± SEM (A) and duration (secs) ± SEM (B) (two-tailed unpaired t-test (A) and two-way ANOVA (B) followed by Newman-Keuls test, *p<0.05).
