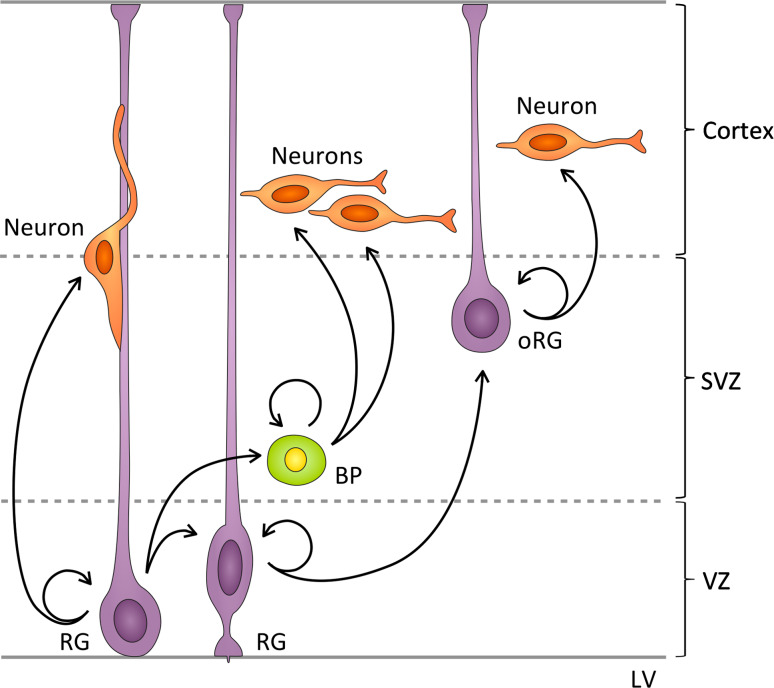
Fig. 2.
Patterns of cell division during mammalian embryonic neurogenesis. During the peak period of murine neurogenesis radial glia (RG) cells divide in the ventricular zone (VZ) mainly asymmetrically, generating one RG cell and one neuron, or one RG cell and one basal progenitor (BP), which migrates to the subventricular zone (SVZ). Asymmetric RG divisions also produce outer RG (oRG) cells, which lose their ventricular attachment and translocate to the SVZ, where they divide asymmetrically to produce neurons