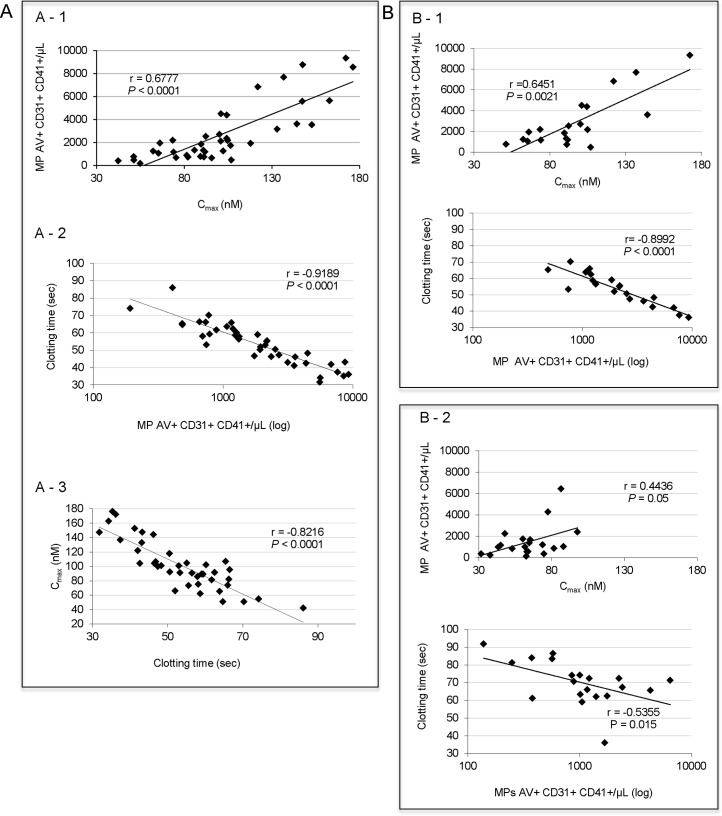
Figure 1. The correlation between the enumeration of PMP assessed by cytometry and phospholipid-dependent procoagulant activity assessed by haemostasis methods.
A- The study was performed in 40 healthy donors and samples were centrifuged according to protocol #1. A1- Comparison of the enumeration of PMP assessed by cytometry and phospholipid-dependent procoagulant activity assessed by CAT method. A2- Comparison of the enumeration of PMP assessed by cytometry and phospholipid-dependent procoagulant activity assessed by STA Procoag PPL® method. A3- Comparison of the two haemostasis methods. B- Study of the effect of a pre-analytical variable, the centrifugation on the comparison of the enumeration of PMP assessed by cytometry and phospholipid-dependent procoagulant activity. Samples from 20 healthy donors were analyzed. B1- Data obtained for centrifugation protocol #1 (6) are similar to data obtained in A1 and A2, respectively with 40 samples. B2- Data obtained for centrifugation protocol #2 (ISTH) do not show correlation between either the enumeration of PMP assessed by cytometry and phospholipid-dependent procoagulant activity assessed by CAT (upper panel) or the enumeration of PMP assessed by cytometry and phospholipid-dependent procoagulant activity assessed by STA Procoag PPL® method (lower panel). P values and r correlation coefficients are given on each histogram. Intra- and inter-assay CV values are less than 3% and less than 14% for STA Procoag PPL® and CAT method, respectively. Intra- and inter-assay CV’s for cytometry using protocol #2 are 7.8 and 9.4%, respectively compared with 6.7% and 5.7% using protocol #1 (7).
(Leroyer et al., 2010, Tsimerman et al., 2011)
1. Leroyer AS, Anfosso F, Lacroix R, Sabatier F, Simoncini S, Njock SM, Jourde N, Brunet P, Camoin-Jau L, Sampol J, Dignat-George F. Endothelial-derived microparticles: Biological conveyors at the crossroad of inflammation, thrombosis and angiogenesis. Thromb Haemost. 2010 Sep;104(3):456–63.
2. Tsimerman G, Roguin A, Bachar A, Melamed E, Brenner B, Aharon A. Involvement of microparticles in diabetic vascular complications. Thromb Haemost. 2011 Aug;106(2):310–21.