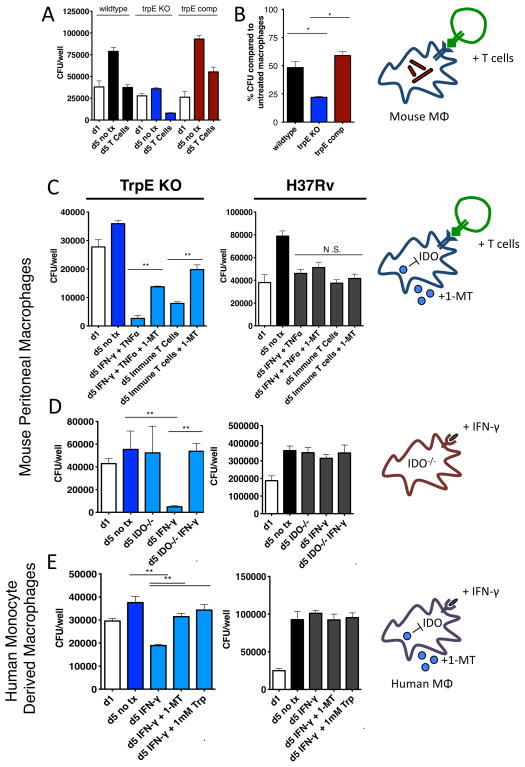
Figure 4.
A. Wild type, tryptophan auxotroph, and complemented strains were used to infect macrophages. One day after infection, macrophages were either stimulated with CD4 T cells in co-culture or remained unstimulated. The tryptophan auxotroph grew poorly in unstimulated macrophages and were hypersuscpetible to the effects of CD4 T cells (B). C. Macrophages were stimulated by either immune CD4 T cells (CD4 T cells isolated from spleens of Mtb-infected mice) or IFN-γ and TNF-α. To test whether the hypersusceptibility of the auxotroph was dependent on IDO, we also inhibited IDO with its small molecule inhibitor, 1-MT, or used macrophages isolated from IDO KO mice (D). E. Human monocyte derived macrophages were infected with wild type and tryptophan auxotroph bacteria. After stimulation with IFN-γ, we showed that the tryptophan auxotroph was also hypersusceptible to the effects of human IFN-γ