Fig. 3.
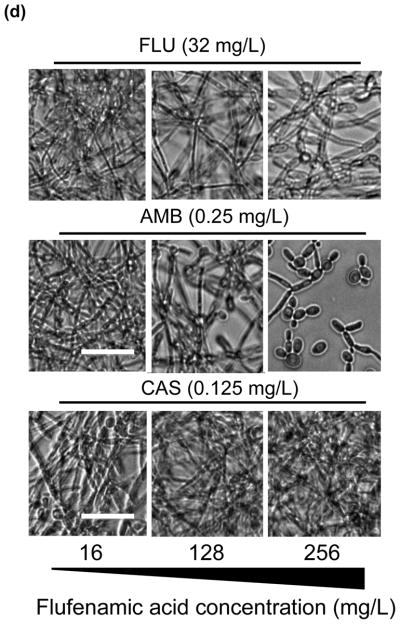
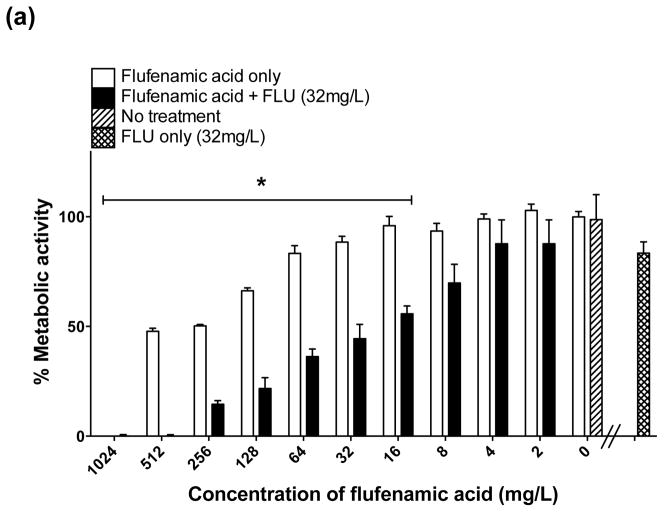
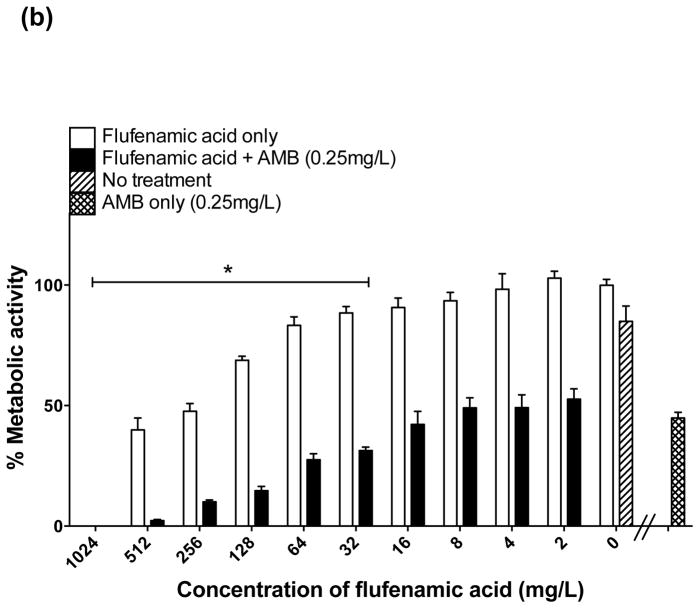
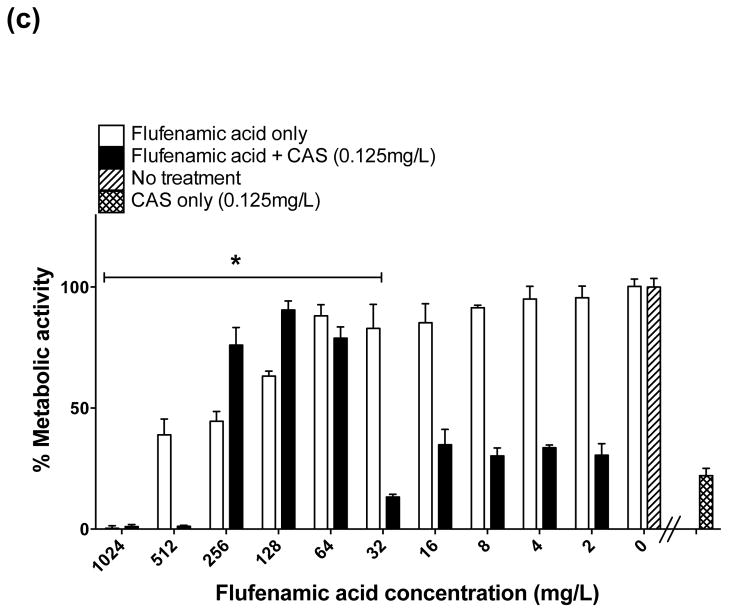
In vitro effect of different concentrations of flufenamic acid (FFA) (2–1024 mg/L) combined with a constant concentration of (a) fluconazole (FLU) at 32 mg/L, (b) amphotericin B (AmB) at 0.25 mg/L and (c) caspofungin (CAS) at 0.125 mg/L for the treatment of mature biofilms. The metabolic activity of drug-free biofilms (no treatment) is shown as a positive control. Graphs represent the average of two experiments performed independently, each time in triplicate. * P < 0.05. (d) Representative light microscopy images of Candida albicans strain SC5314 biofilms. FFA was added at different concentrations combined with constant concentrations of FLU (32 mg/L), AmB (0.25 mg/L) or CAS (0.125 mg/L) for treatment of mature biofilms. Visual differences in biofilm architecture are apparent at three different FFA concentrations (16, 128 and 256