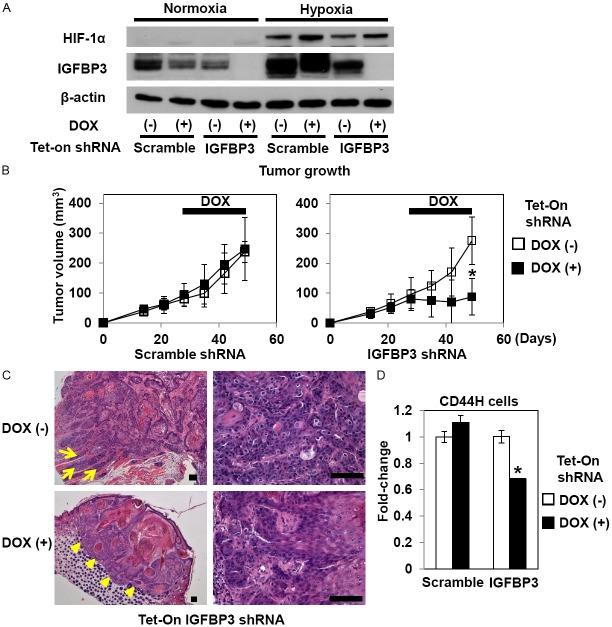
Figure 2.
IGFBP3 knockdown inhibits TE11 xenograft tumor growth and reduces intratumoral CD44H cells. (A) TE11 cells with Tet-On shRNA directed against IGFBP3 or a non-silencing sequence (scramble) were exposed to either hypoxia or normoxia in the presence or absence of 0.5 μg/ml DOX for 48 h for documentation of the RNAi effect upon IGFBP3 expression. Western blotting was done to evaluate indicated molecules with β-actin as a loading control. In (B-D), TE11 derivatives with indicated genotypes were xenografted. Mice were administered drinking water with or without DOX starting at day 28 for 3 weeks to be sacrificed at day 49. Tumor growth (B), histology (hematoxylin and eosin staining) (C) and intratumoral CD44H cells (D) were evaluated. Note that in (C), the tumor without IGFBP3 knockdown [top panels, DOX (-)] shows an invasive growth pattern as indicated by tumor cell nests extending into the adjacent muscle layers (arrows, top left panel) and poorly differentiated atypical cells exhibiting mitotic figures (top right panel). By contrast, the tumor with IGFBP3 knockdown [bottom panels, DOX (+)] is well-circumscribed as demarcated by arrow heads (bottom left panel) and contains more differentiated cells with fewer mitotic figures (bottom right panel). In (D), enzymatically dissociated TE11 cells were isolated from xenograft tumors for FACS analysis. *, P<0.05 vs. DOX (-); n=8 in (B) and n=3 in (D). Scale bar, 100 μm in (C).