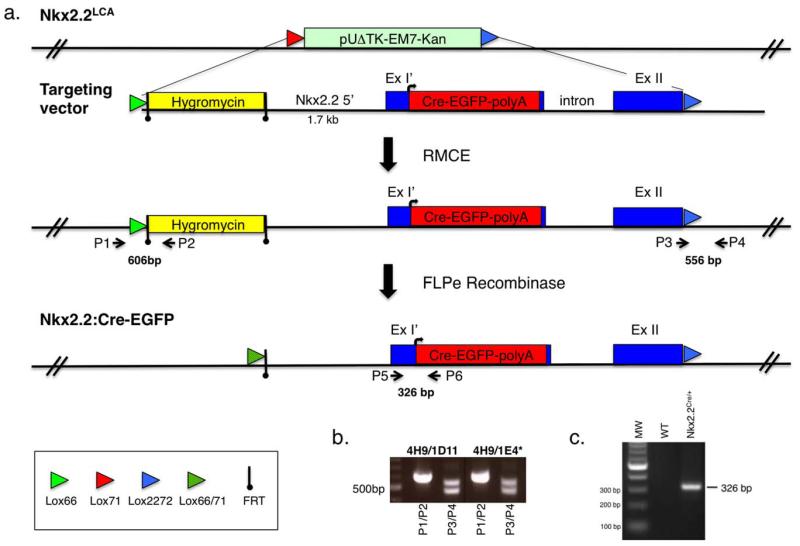
FIG. 1.
Generation of the Nkx2.2:CreEGFP knockin allele. (a) Schematic of the strategy used to create the Nkx2.2:CreEGFP knockin allele. Nkx2.2LCA refers to the RMCE Nkx2.2 acceptor allele integrated into the genomic locus of the 4H9 ES cell line (Arnes et al., 2012). The RMCE lox sites are indicated by colored arrows. The targeting vector includes a FRT flanked hygromycin cassette for positive selection of the targeting event. The CreEGFP gene was recombinered in frame at the Nkx2.2 ATG codon and deleted most of coding exon 1. ExI’ signifies the truncated region of Nkx2.2 coding exon 1 and ExII refers to the Nkx2.2 coding exon 2. The CreEGFP cassette replaces the Nkx2.2LCA allele using RMCE. P1 and P2 indicate the 5′ PCR primers that verify integration of the hygromycin cassette into the correct genomic locus. P3 and P4 indicate the 3′ primers that distinguish the wild-type Nkx2.2 allele and the newly integrated Nkx2.2:CreEGFP allele containing the 2722 lox site. The Flpe-recombinase is used to remove the FRT-flanked hygromycin cassette. P5 and P6 refer to the genotyping primer set used to determine for the presence of the Nkx2.2:CreEGFP allele. (b) Representative PCR amplification results of Nkx2.2LCA ES cells containing RMCE-mediated recombination of the Nkx2.2:CreEGFP allele. For each RMCE ES cell clone, two sets of primers (P1/P2 and P3/P4) were used. Primers 1 and 2 detect a 606 bp product. Primers 3 and 4 detect a 556 bp for the Nkx2.2:CreEGFP allele and 479 bp for the Nkx2.2 wild-type allele. (c) Representative PCR amplification results of Nkx2.2:CreEGFP mice and wild-type littermates. Primer P5 and P6 amplify a 326 bp band from only the mice carrying the Nkx2.2:CreEGFP allele.