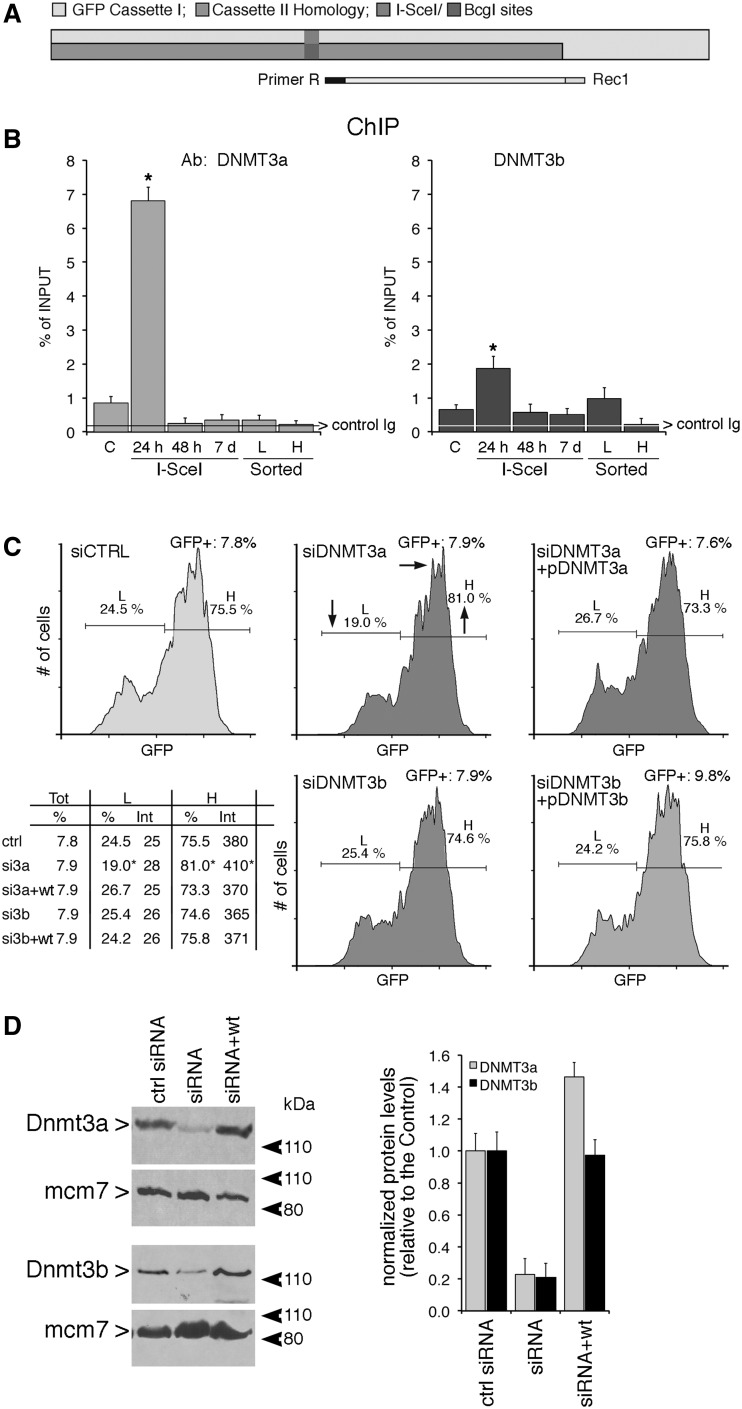
Figure 5.
DNMT3a and 3b are recruited to the DSB early during repair, but only DNMT3a is necessary for generation of L cells (A and B) Recruitment of DNMT3a, DNMT3b to the I-SceI chromatin. Cells were transfected with I-SceI and 24 h, 48 h or 7 days later, were fixed, collected, chromatin-extracted and subjected to ChIP analysis with specific anti-DNMT3a and DNMT3b antibodies. The specific primers used to amplify the GFP cassette I are indicated in (A). Data represent the fraction of immunoprecipitated DNA relative to the input chromatin-DNA present in the reactions (% of input; mean ± SD; n ≥ 9); the average of immunoprecipitated DNA with a control Ig is reported on each bar graph. *P < 0.01, paired t test. (C) Silencing the expression of DNMT3a reduces L cells. Cells were electroporated with the siRNA targeting DNMT3a and DNMT3b (see ‘Materials and Methods’ section and protocol S1) and analyzed 7 days later, when L and H cells were clearly separated. On the bottom left panel, statistical analysis derived from three independent experiments is shown. *P < 0.01, paired t-test comparing GFP intensity, Chi Square (χ2) comparing the percentage of L/H cells. The horizontal and vertical arrows in the central inset indicate the shift in fluorescence intensity and in the distribution of L and H cells, respectively. Treatment with 5azadC (10 µM for 2 days, 48 h after I-SceI transfection) rescued completely the loss of L cells (intensity and % GFP+ cells) induced by DNMT3a overexpression in siDNMT3a-silenced cells (data not shown). (D) Western blot analysis of DNMT3a and 3 b in silenced cells. Total cell extracts were prepared 48 h after electroporation and analyzed by immunoblot with the specific antibodies indicated. On the right is shown quantitative analysis derived from three immunoblots (mean ± SD).