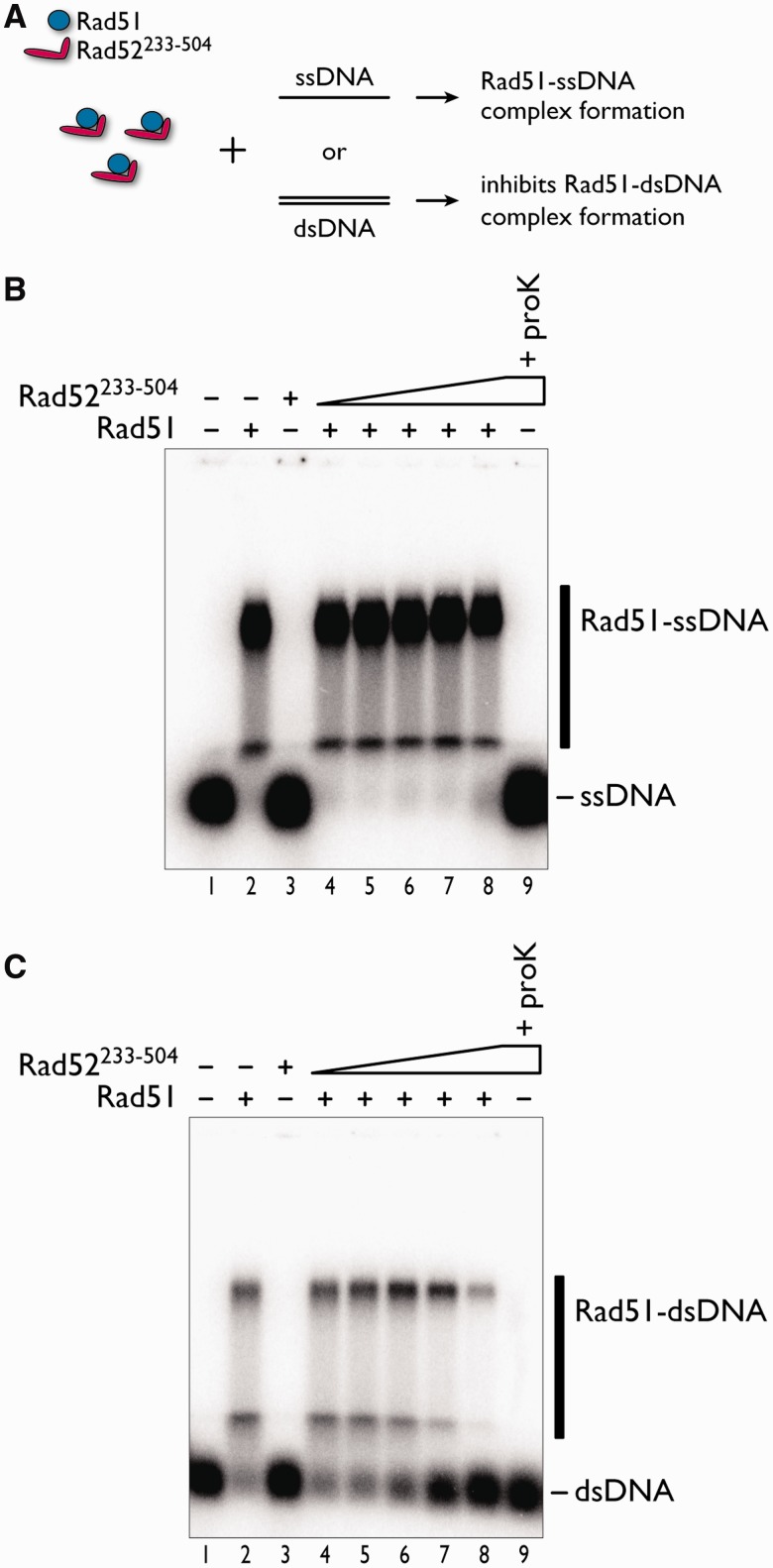
Figure 2.
Effects of Rad52233–504 on the formation of Rad51–ssDNA and Rad51–dsDNA complexes. (A) Schematic representation of the assay. ssDNA (1 µM in nucleotides) (B) or dsDNA (1 µM in nucleotides) (C) was added to the reaction mixture containing Rad52233–504 and Rad51 (1 µM). Products were stabilized by glutaraldehyde fixation and fractionated through an agarose gel. The fixed Rad51–DNA complexes migrated to two major locations in the gel (B and C, lane 2). Increases in the Rad52233–504 concentration caused greater increases in the unbound dsDNA, rather than the unbound ssDNA (B and C, compare lanes 6–8). The Rad52233–504 concentrations were 0.5 µM (lane 4), 1 µM (lane 5), 2 µM (lane 6), 4 µM (lane 7) and 8 µM (lanes 3, 8 and 9). Lanes 3 and 9 are identical, except for the addition of proteinase K after glutaraldehyde fixation.