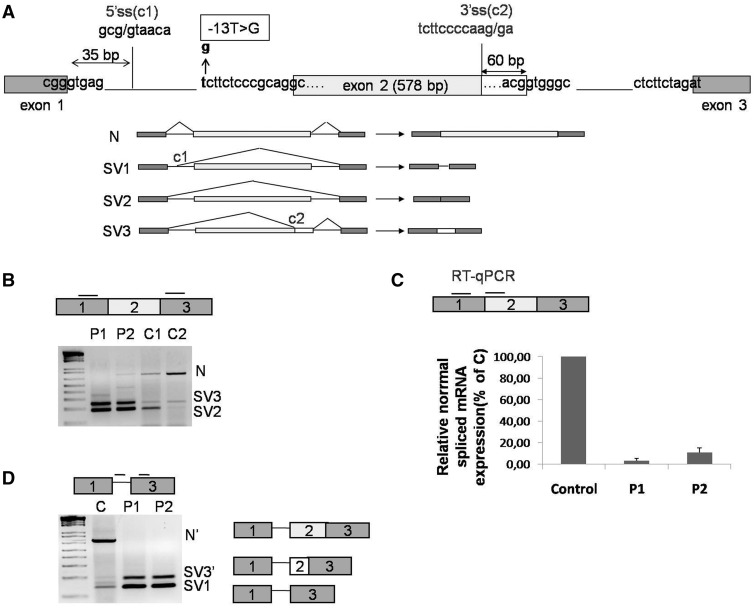
Figure 1.
GAA mRNA splicing variants expressed in cultured fibroblasts. (A) Schematic representation of the 5′ region of the GAA gene (exons 1–3). The position of the c.-32-13T>G mutation is highlighted in bold. The cryptic splice sites located at position +35 from the normal donor splice site of exon 1 and at −60 nt from the donor site of exon 2 are shown as C1 and C2, respectively. Lower panel, schematic diagram of the GAA mRNA spliced variants already described in human fibroblasts: N, SV1, SV2 and SV3. (B) RT-PCR analysis of the region encompassing exons 1–3 of GAA mRNA in fibroblasts from patients carrying the c.-32-13T>G mutation (P1 and P2) and normal controls (C1 and C2). Three fragments corresponding to normal (N) and SV2 and SV3 variants were detected in fibroblasts both from patients and controls. (C) real time PCR quantification of the normal spliced GAA mRNA (N) in fibroblasts from patients P1 and P2 and a normal control. Normal spliced GAA mRNA in P1 and P2 fibroblasts is expressed as percentage of the normal spliced mRNA detected in the normal control. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. (D) RT-PCR analysis of GAA mRNA using primers to specifically amplify SV1 variant in fibroblast from patients P1 and P2 and from a normal control. In addition to the SV1 variant, other two PCR fragments identical to N and SV3 but retaining the first 35 nt of intron 1 were detected (N′ and SV3′).