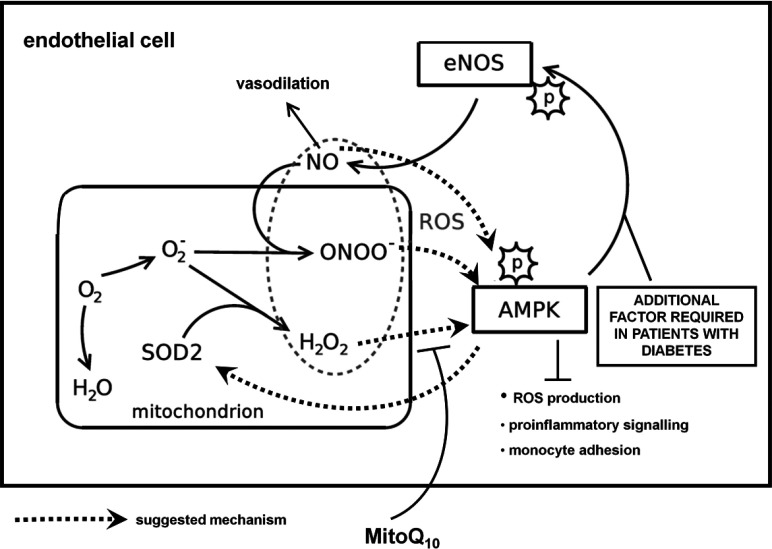
Figure 6. Proposed mechanism of mtROS-mediated AMPK activation in endothelial cells.
The results suggest a potentially mtROS-mediated increase in AMPK activity in patients with CAD and T2D. The mtROS in question are likely to be downstream derivates of H2O2, such as lipid peroxidation products. AMPK may therefore be part of a feedback or adaptive mechanism with a role in defence against oxidative stress in the endothelium, attenuating pro-inflammatory signalling and regulating expression of antioxidant genes, including SOD2. However, increased kinase activity does not appear to be sufficient to stimulate activation of eNOS, in patients with T2D.