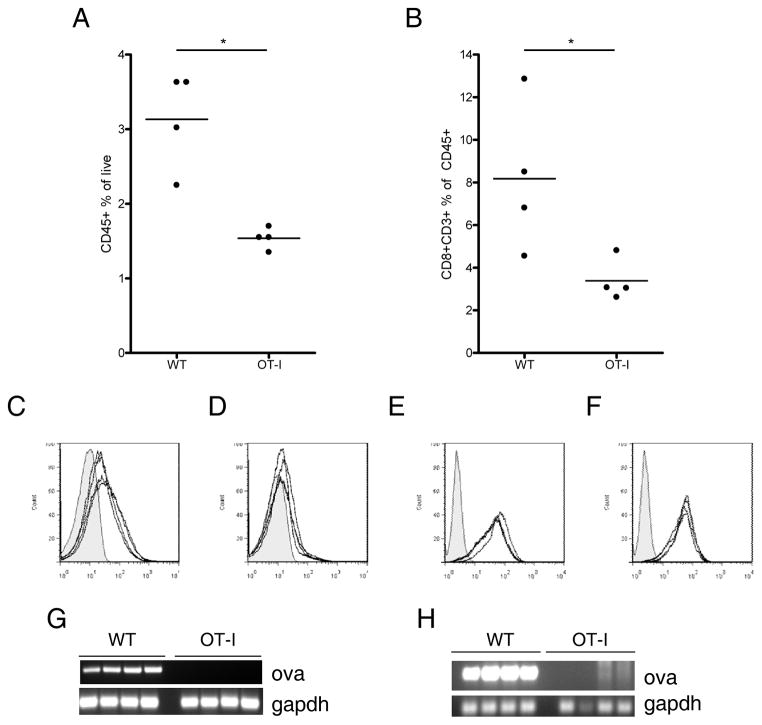
Figure 2. B16ova tumors which escape in OT-I mice display several characteristics distinguishing them from tumors in WT mice.
10 mm tumors were harvested from WT or OT-I mice, homogenized, and analyzed by flow cytometry and PCR. A, Tumor homogenates were stained for CD45 to identify infiltrating immune cells. B, CD45+ cells in A were analyzed for expression of CD8 and CD3 to identify tumor-infiltrating CTL. C and D, Expression of H-2Kb on the CD45− cells of tumors freshly excised from WT (C) or OT-I mice (D). Histograms show a shaded isotype control and H-2Kb levels of 4 individual tumors. E and F, tumors were re-established in culture, treated with 500 U/mL IFNγ to induce MHC expression, and stained for H-2Kb. H-2Kb expression on tumor lines which came from WT (E) or OT-I (F) mice. RNA and DNA were isolated from freshly excised tumors and tested for ova and gapdh by RT-PCR (G) or PCR (H). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.