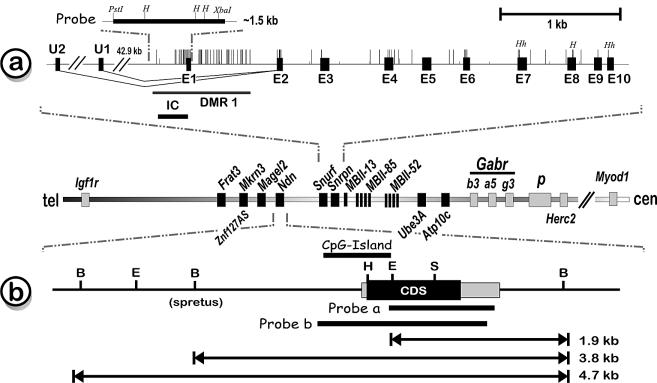
Figure 1.
(a) Structure of the bicistronic Snurf/Snrpn gene within the imprinted neuronal gene cluster on mouse chromosome 7C. Deletion, uniparental disomy (UPD) or inappropriate imprinting of the homologous chromosomal region in humans results in the neurogenetic PWS. Deletion of the DMR1 in mice, which spans the promoter and exon1 of Snurf/Snrpn, results in the disability to maintain the correct paternal methylation imprint during embryonic development (reviewed in 7). The bicistronic structure of this gene leads to two different protein products, SNURF and SmN. Vertical lines represent CpG dinucleotides. (b) Genomic structure of the intronless Ndn gene about 1 Mb telomeric to the IC. Ndn has DNA binding capacity and may play a role as a growth suppressor that interacts with the transcription factors E2F1 and p53 in virtually all post-mitotic neurons in the brain. H, HpaII/MspI; E, EagI; S, SacII; B, BglII; BS, polymorphic BglII site to identify the parental origin of an allele in mice with mixed genetic background.