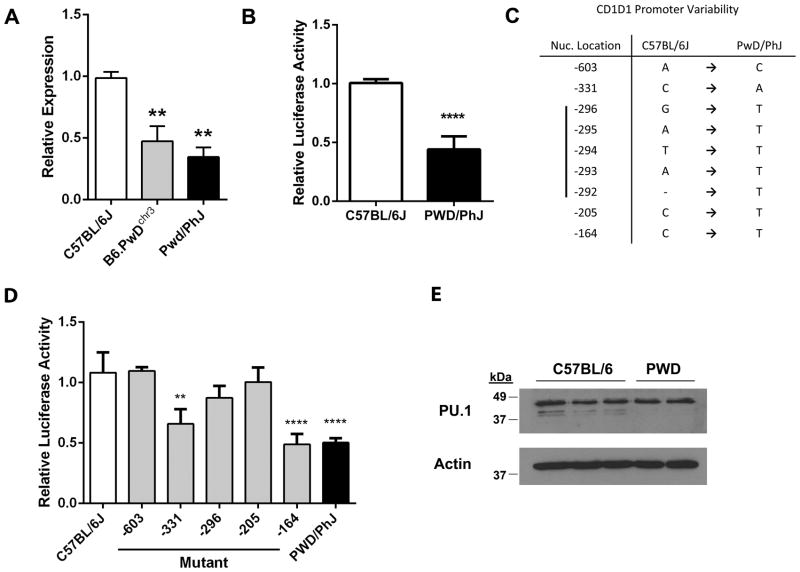
Fig. 6. Decreased CD1d gene expression in PWD/PhJ is associated with SNPs in the CD1d promoter.
(A) Comparison of CD1d gene expression among age-matched, sex-matched B6, PWD, and B6.PwDchr3 strain thymocytes using qPCR. Beta-2 microglobulin was used as an endogenous control. Relative expression was calculated using a standard curve. All data are normalized to C57BL/6J mice. Data represent the means ± s.d., n = 2–3 mice per strain, **p ≤ 0.01, and are representative of two separate experiments. (B) Comparison of B6 and PWD CD1d promoter activity. The proximal ~700 bp of the B6 and PWD CD1d promoters were transfected into mouse L929 cells, after which activity was assessed using a luciferase reporter assay. The data represent the means ± s.e.m. and are the combined data of two separate experiments, ****p < 0.0001. (C) Location of nucleotide differences between B6 and PWD CD1d promoters. Positions are indicated relative to the A (+1) in the start codon. (D) Relative contribution of the PWD CD1d promoter SNPs to impaired promoter activity. Site-directed mutagenesis was used to create successive B6 to PWD mutations. The exception was the -296 to -292 region of CD1d which was mutated in its entirety (denoted as -296). B6 and PWD promoters were subcloned into a luciferase reporter construct and transiently transfected into murine L929 cells. Data represent the means ± s.d., n = 6 measurements, **p ≤ 0.01, ****p ≤ 0.0001 denote significant differences as compared to the C57BL/6J wild-type promoter, and are representative of two separate experiments. (E) Comparison of PU.1 expression between B6 and PWD thymocytes. PU.1 protein expression was assessed in thymocyte preparations from B6 (n=3) and PWD (n=2) mice, using Western blot. Each lane represents a thymocyte preparation from a single mouse. Actin expression was measured for use as a loading control.