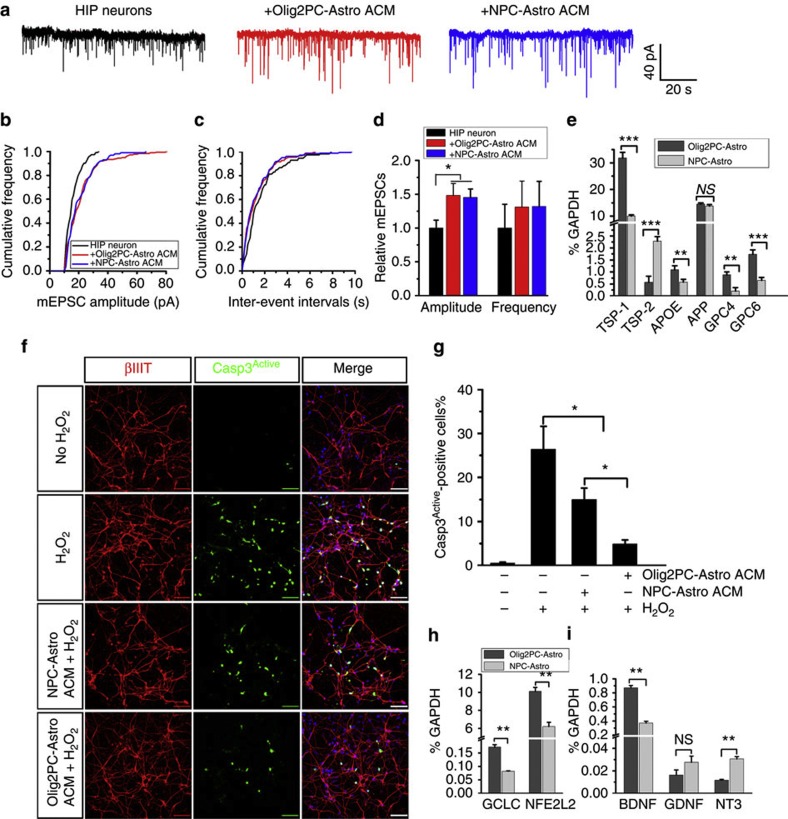
Figure 4. Effects of ACM from Olig2PC-Astros and NPC-Astros on neurons.
(a) Examples of mEPSC recordings from primary hippocampal (HIP) neurons and HIP neurons fed with ACM from Olig2PC-Astros or NPC-Astros. (b and c) Normalized cumulative curves showing the effects of ACM on the amplitude and frequency of mEPSCs from the sample neurons. (d) Statistical results demonstrating that the amplitude is significantly increased by adding ACM from both Olig2PC-Astros and NPC-Astros, but the frequency is not changed. Each column represents the averaged value from seven neurons (n=7). (e) RT-PCR analysis of the expression of the genes encoding factors that are crucial for regulating synapse formation and function, which includes TSP-1 and 2, APOE, APP and GPC4 and 6. (f) βIII tubulin and activated caspase-3 co-staining of hESC-derived neurons treated with medium alone or medium plus H2O2, NPC-Astro ACM plus H2O2 and Olig2PC-Astro ACM plus H2O2. Blue, DAPI-stained nuclei. Scale bars represent 50 μm. (g) Quantification of βIII tubulin+ and activated caspase-3+ cells among the groups with different treatments (n=4). One-way ANOVA test; *P<0.05. (h and i) RT-PCR analysis of the expression of the antioxidant defense-related genes, GCLC and NFE2L2 (n=3), and the neurotrophic growth factor genes, BDNF, GDNF and NT-3 (n=3). Student’s t-test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. NS represents no significance. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m.