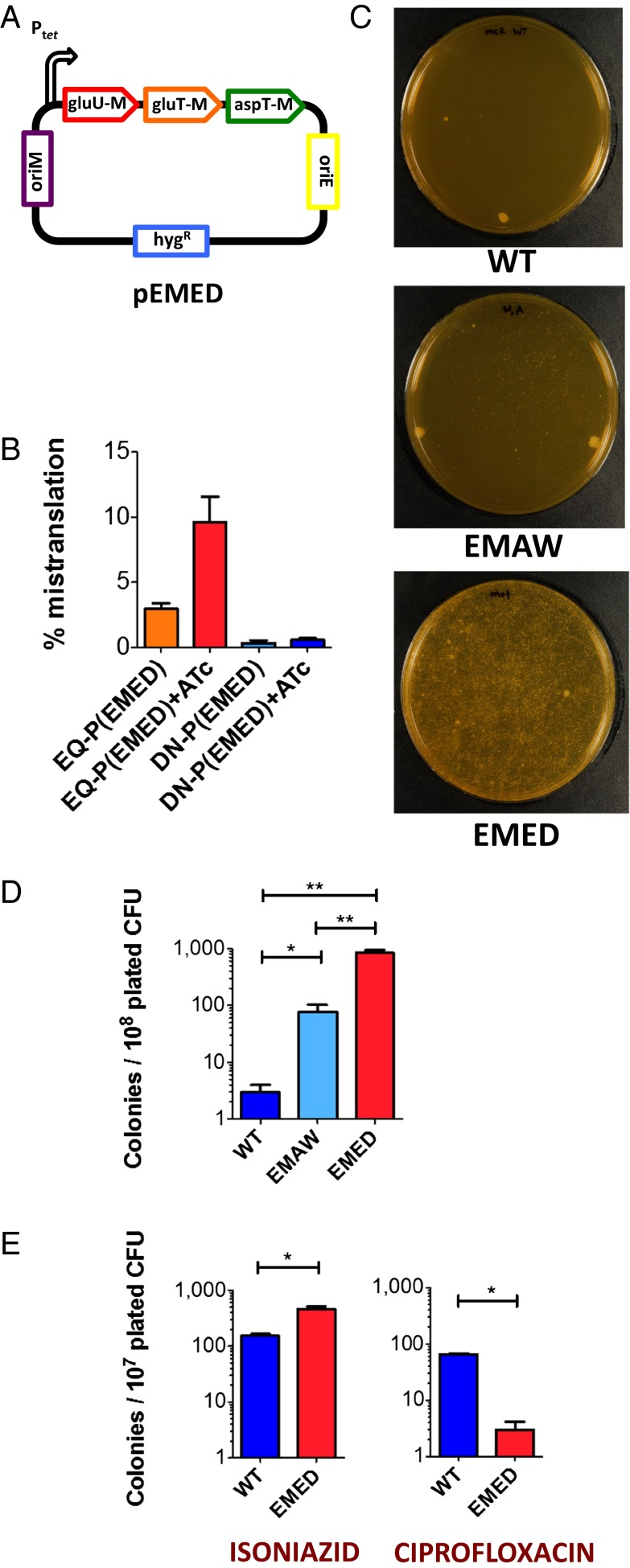
Fig. 1.
High rates of mycobacterial mistranslation result in phenotypic drug resistance to rifampicin and isoniazid. (A) Schematic of tRNA anticodon swap construct. The anticodons of gluU, gluT, and aspT tRNAs were mutated to that of glnU, glnT, and asnT, respectively. The tRNAs were cloned into a mycobacterial expression plasmid under control of a tetracycline promoter and transformed into WT M. smegmatis mc2-155 to make strain EMED. Strain EMAW, which misincorporates alanine for tryptophan, was made by a similar strategy by mutation of the anticodon of tRNAAla. (B) Strain EMED has a basal mistranslation rate of ∼3% per codon for aspartate for asparagine, rising to ∼10% per codon upon induction of expression with anhydrotetracycline (ATc). Materials and Methods provides a description of the mistranslation reporter assay used to calculate mistranslation rates. WT M. smegmatis or mistranslating strains EMED and EMAW were plated on rifampicin media (100 µg/mL) (C and D) or isoniazid (30 µg/mL) or ciprofloxacin (0.5 µg/mL) media (E) and incubated at 37 °C for 5 d. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Student t test).